Figure 2.
Hallmarks of naive pluripotency in transcriptome, X chromosome reactivation, and global DNA methylation
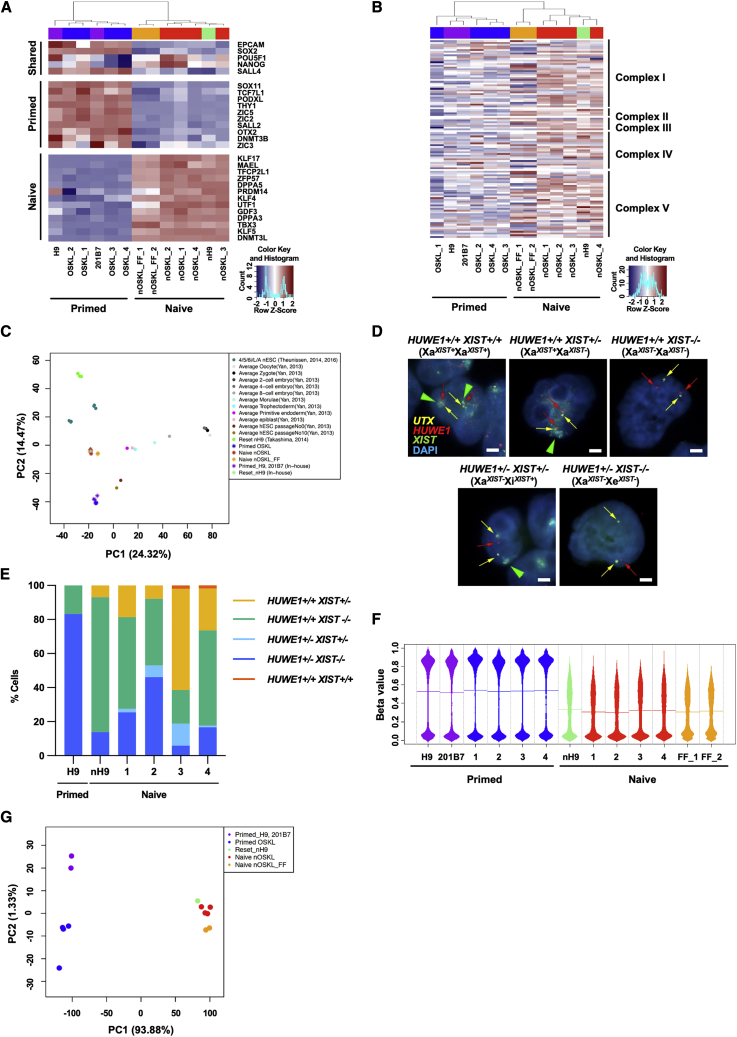
(A) Heatmap of the RNA-seq data depicting expression levels of shared, primed, and naive pluripotency-associated marker genes in naive and primed human PSCs.
(B) Heatmap of genes encoding proteins of the electron transport chain located in the inner membrane of mitochondria. These genes reflect the activity of oxidative phosphorylation, are classified by the mitochondrion complex, and are hierarchically clustered.
(C) PCA of RNA-seq data from primed and naive human PSCs in this study compared with reset naive human iPSCs and pre-implantation embryo samples from Takashima et al., 2014, Theunissen et al., 2014, and Yan et al., 2013.
(D) Representative RNA-fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) images of naive and primed human iPSCs detecting X-linked genes UTX (escapes X chromosome inactivation) and HUWE1 and XIST (subject to X chromosome inactivation). UTX was analyzed to ensure only PSCs with normal X chromosome were included in the quantification. Scale bar, 20 μm.
(E) Quantification of the RNA-FISH patterns for XIST with HUWE1 in cells with biallelic UTX expression. 100 cells were analyzed in each cell line. Most naive human iPSCs showed X reactivation as indicated by the biallelic HUWE1 expression. Some cells in nOSKL_3 and 4 exhibited biallelic XIST expression, which is similar to the expression pattern of pre-implantation epiblast (Sahakyan et al., 2017; Theunissen et al., 2016).
(F) Beanplot of the global DNA methylation levels in primed and naive human PSCs analyzed using DNA methylation arrays. Horizontal lines in the beanplot represent mean methylation beta values.
(G) PCA of global DNA methylation in primed and naive human PSCs using DNA methylation arrays.