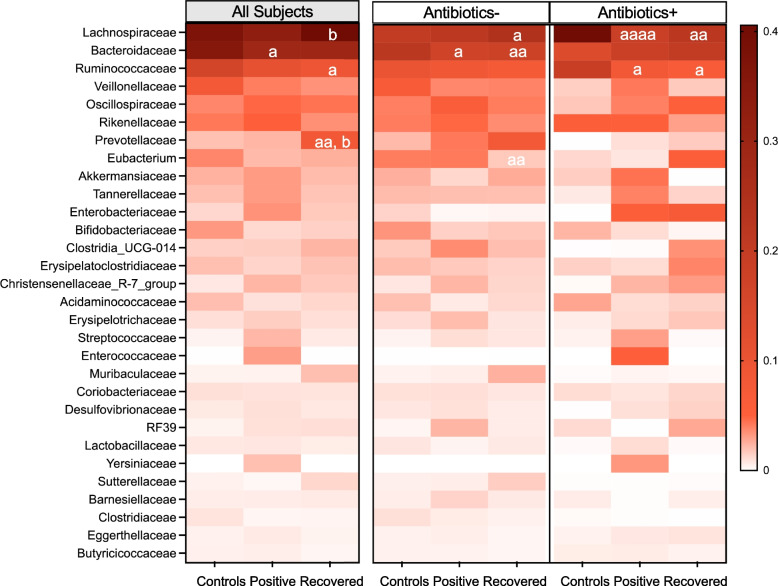
Fig. 3.
Heatmap of gut microbial compositions in the three groups of study subjects that varied in COVID-19 infection status. The relative abundances of the 30 most abundant bacterial taxa at the family level were compared between the Controls (n = 20), COVID-19-positive (n = 20), and COVID-19-recovered patients (n = 20) (left panel). Additional comparisons were performed in subjects without (center panel) or with recent antibiotic use (right panel). Table 1 indicates the number of subjects in each group. Left panel: statistical significance was assessed for comparisons to all Controls (a) or to all COVID-19-positive patients (b). For particular taxa: ap < 0.05, bp < 0.05, and aap < 0.01, by two-way ANOVA. Right panel: p-values are shown for comparisons to the Controls (a) only between subjects of the same antibiotic use status. Bacterial communities in the COVID-19-positive and COVID-19-recovered patients did not differ substantially, as determined by two-way ANOVA. For particular taxa: ap < 0.05, aap < 0.01, and aaaap < 0.0001, by two-way ANOVA