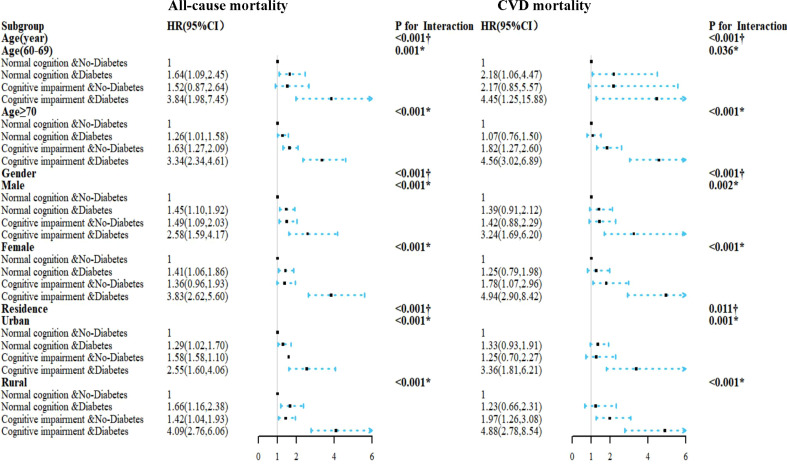
Figure 2.
HRs for the combined associations of cognition impairment and diabetes mellitus with all-cause and CVD mortality according to the classification of age, gender, and residence. All models were adjusted for age (not in the age subgroup) and gender (not in the gender subgroup), residence (not in the residence subgroup), education, marriage, smoking status, alcohol drinking, exercise, BMI, WC, chronic diseases (hypertension, dyslipidemia, coronary disease, COPD, and tumor), TC, TG, and uric acid. The estimated HRs for each group are compared with normal cognition and non-diabetes groups. †Interaction between the four-level joint variable of CI/DM and age, gender, or residence subgroup on mortality. *Interaction between diabetes mellitus and cognitive impairment on mortality.