Figure 3.
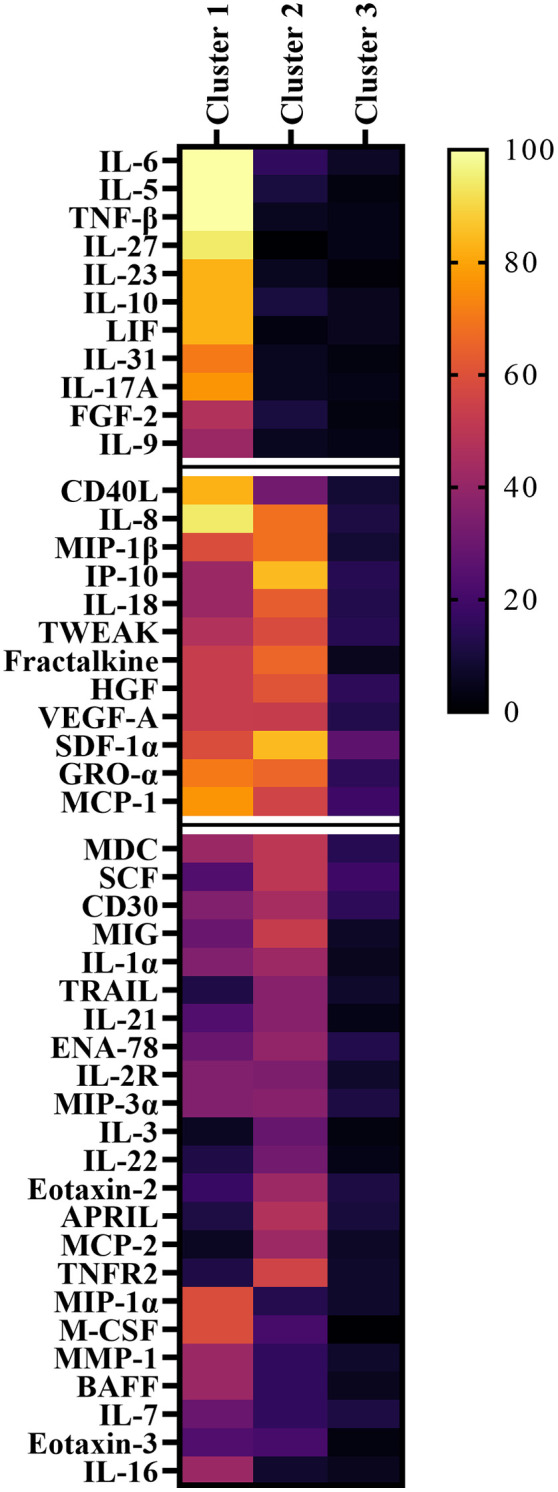
Heatmap of significantly altered cytokines, chemokines and related molecules showing the frequency of samples above the 90% specificity cut-off values for MS. Samples are classified in cluster 1 to 3 by k-means cluster analysis. Cytokines and chemokines are organized according to their frequency within the clusters. APRIL, a proliferation-inducing ligand; BAFF, B cell activation factor; BLC, B lymphocyte chemoattractant; CD40L, CD40 ligand; ENA-78, epithelial neutrophil-activating peptide-78; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; GRO, growth-regulated oncogene; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; IP, interferon-ɣ-induced protein; I-TAC, interferon-inducible T cell α-chemoattractant; LIF, leukemia inhibitory factor; MCP, monocyte chemoattractant protein; M-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; MDC, macrophage-derived chemokine; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; MIG, monokine induced by interferon-ɣ; MIP, macrophage inflammatory protein; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MOGAD, myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein associated disease; MS, multiple sclerosis; NGF, nerve growth factor; NMOSD, neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder; SCF, stem cell factor; SDF, stromal cell-derived factor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TRAIL, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin; TWEAK, tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
