Figure 3.
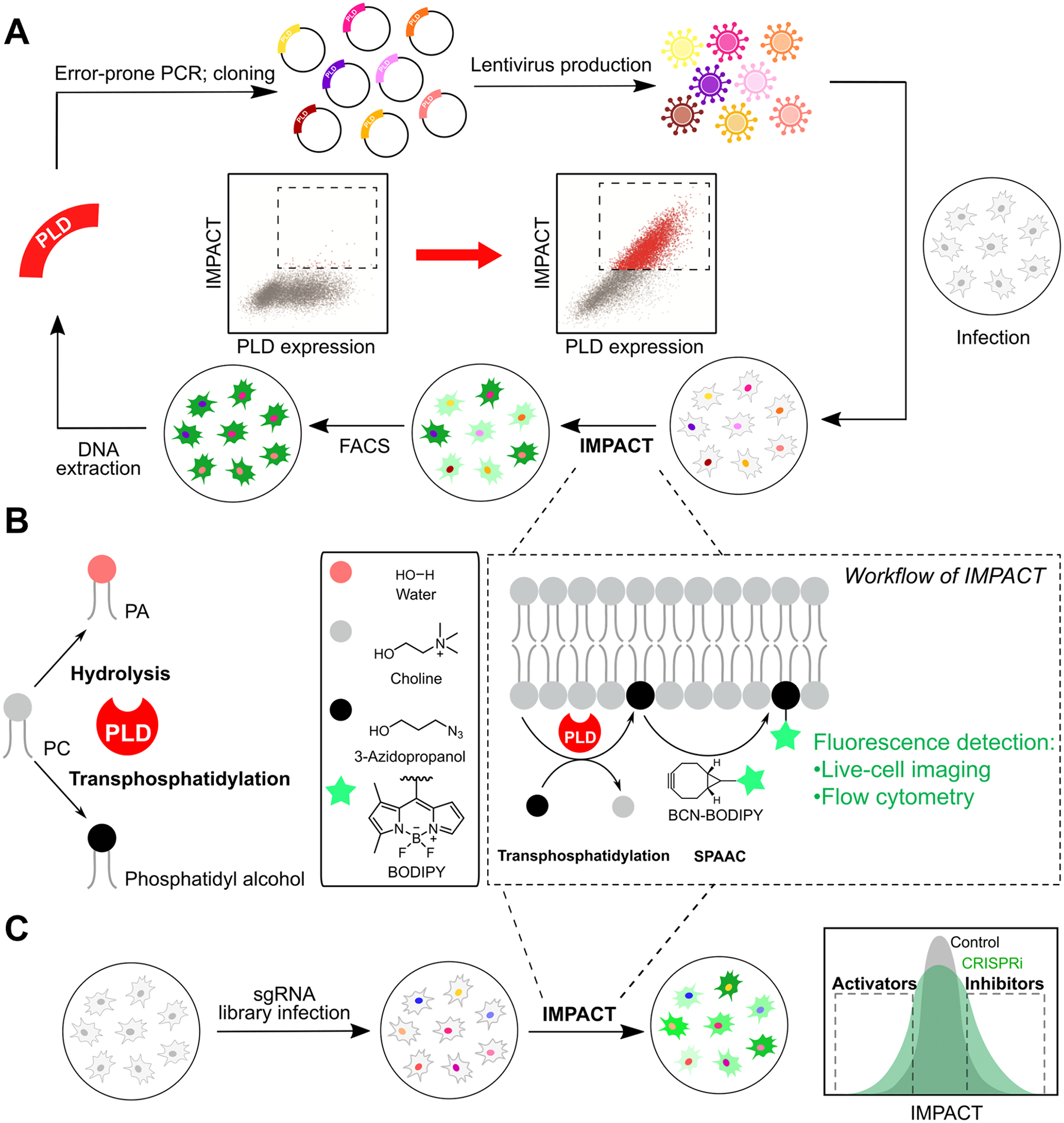
Imaging PLD Activity with Clickable Alcohols via Transphosphatidylation (IMPACT). (A) Activity-based directed evolution of superPLDs with higher catalytic activities in mammalian cells using error-prone PCR and an IMPACT-based enrichment strategy. (B) The concept underlying IMPACT. PLDs can catalyze two reactions of PC: hydrolysis to form PA and transphosphatidylation with primary alcohols to form phosphatidyl alcohols. By using transphosphatidylation with bioorthogonal alcohols such as 3-azido-1-propanol followed by tagging with a bicyclononyne (BCN)-BODIPY fluorophore via the strain-promoted azide–alkyne cycloaddition (SPAAC) bioorthogonal reaction, IMPACT enables generation of fluorescent phosphatidyl alcohol lipids as reporters of cellular PLD activity. (C) Platform for discovery of new activators and inhibitors of mammalian PLD signaling by coupling pooled, genome-wide CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) screening with IMPACT labeling, fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) enrichment, and short guide RNA (sgRNA) sequencing.
