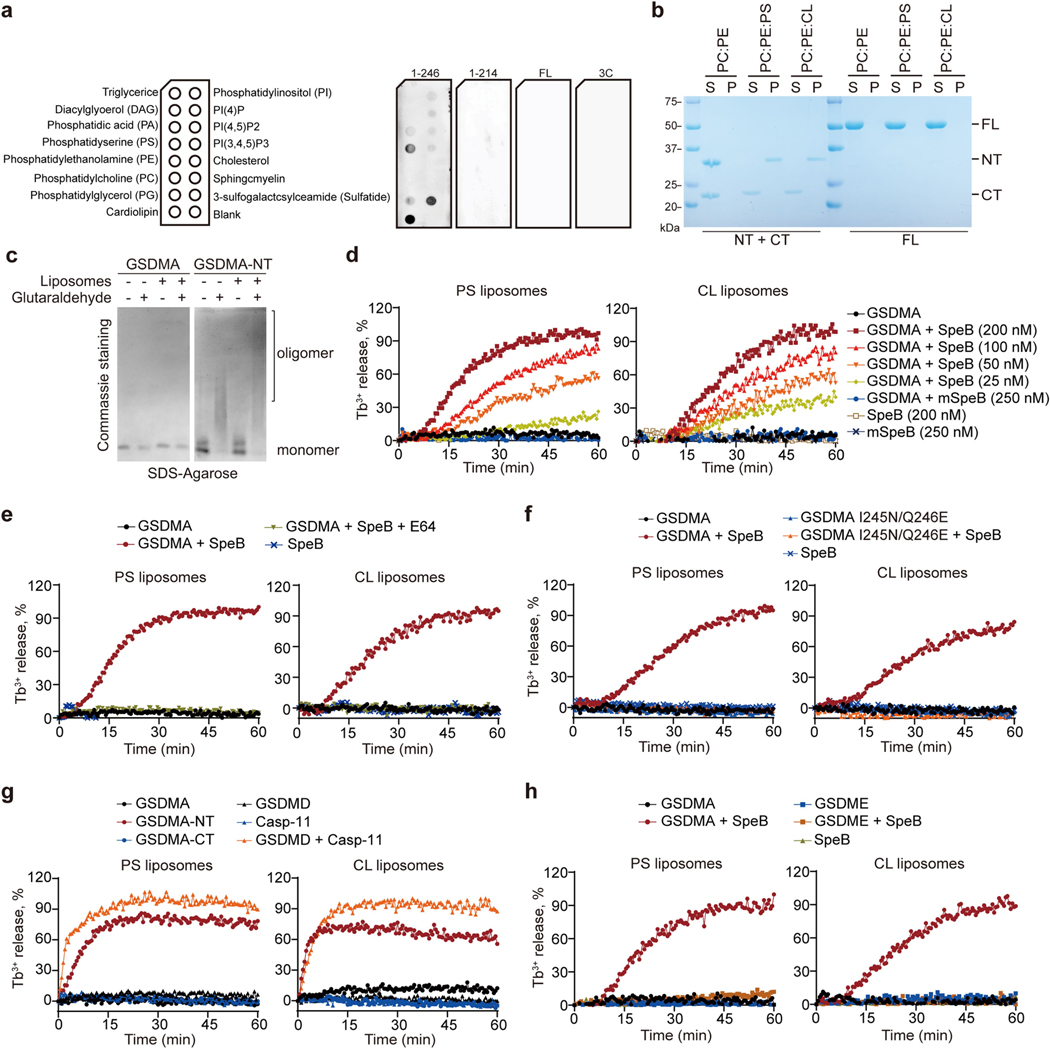
Extended Data Fig. 8 |. Phospholipid binding property and liposome-disrupting activity of GSDMA-NT.
a, Lipid strips dotted with indicated phospholipids (left panel) were incubated with noncovalent complex of cleaved GSDMA with a Flag-tag inserted right before the cleavage site, unprocessed full-length GSDMA, or 3C protease, followed by immunoblot analysis with an anti-Flag antibody (right panel). b, Indicated liposomes incubated with noncovalent complex of cleaved GSDMA (NT + CT) and full-length GSDMA (FL) were subjected to sedimentation by ultracentrifugation. Proteins in both liposome-free supernatant (S) and liposome-containing pellet (P) were analysed by SDS-PAGE. c, Indicated recombinant proteins incubated or not with CL liposomes and glutaraldehyde were analyzed by SDS-agarose gel electrophoresis and subsequent Coomassie Blue staining. d–h, Leakage of PC-PE liposomes containing additional PS or CL was monitored in real-time by terbium (Tb3+) fluorescence after incubation with recombinant gasdermins proteins in the presence or absence of recombinant SpeB or enzymatically inactive SpeB C192S (mSpeB) as indicated, or cysteine protease inhibitor E64 if necessary. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1.