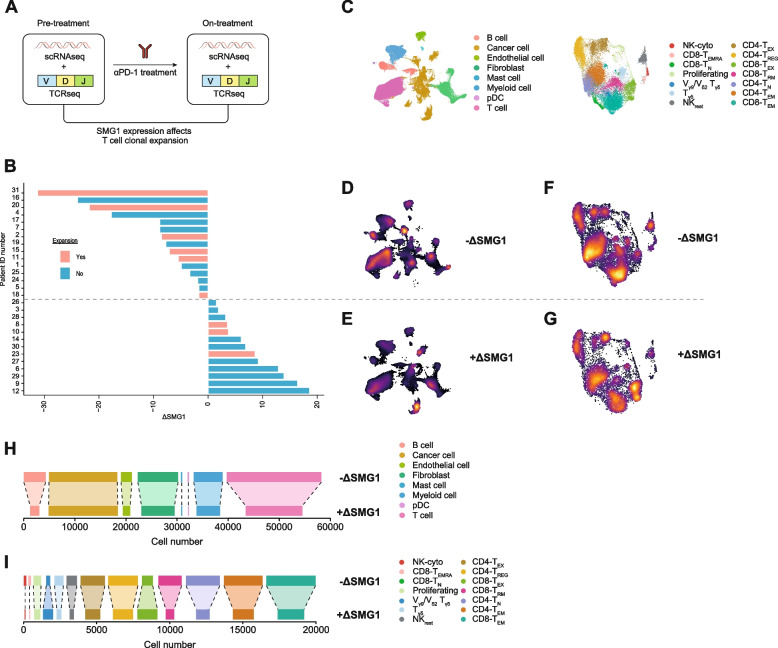
Fig. 4.
SMG1 upregulation after anti-PD-1 therapy associates with reduced immune infiltration and compromised T-cell expansion in breast cancer patients. (A) Study design from [21] used to interrogate whether SMG1 expression fluctuation during anti-PD-1 treatment affect at TCR clonal expansion in breast cancer patients (n = 28) (B) Fluctuation of SMG1 expression (ΔSMG1) in breast cancer patient during the course of anti-PD1 treatment. Patients determined with positive TCR clonal expansion after anti-PD1 treatment are depicted in red. (C) Legend for the different cell types assigned in the UMAP clusters. (D) Represent the UMAP intensity of the group of patients with reduction on SMG1 expression after anti-PD-1 treatment (-ΔSMG1) (E) Represent the UMAP intensity of the group of patients with enhance SMG1 expression after treatment (+ΔSMG1). (F) Represent the UMAP intensity from the tumor immune infiltrate of the group of patients with reduction on SMG1 expression after anti-PD-1 treatment (-ΔSMG1). (G) Represent the UMAP intensity from the tumor immune infiltrate of the group of patients with enhance SMG1 expression after treatment (+ΔSMG1). (H) Bar plot showing absolute cell numbers of each population shown in (D-E). (I) Bar plot showing absolute cell numbers of each population shown in (F-G)