Figure 3.
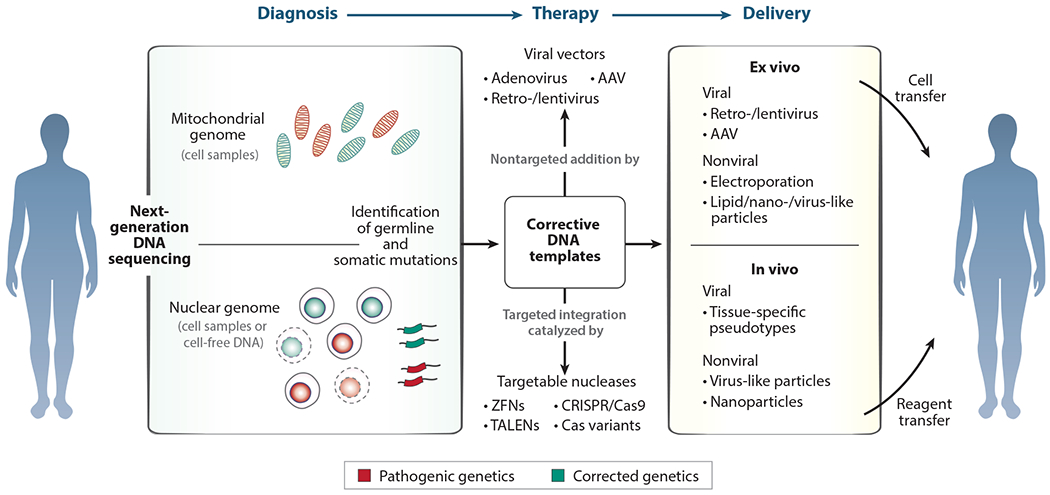
Modular systems for genetic diagnosis and therapy. Gene therapies in all four human genetic compartments depend on the modular process of diagnosis, therapeutic design, and compartment-specific delivery of therapeutic reagents. Diagnosis of genetic disease is now centered around next-generation DNA sequencing to detect errors in the mitochondrial and nuclear genomes. Therapy can be based on bulk replacement or selection of the genetic compartment or the therapeutic nontargeted addition of new genetic material or targeted correction of causative mutations through gene editing. Delivery platforms targeting each genomic compartment in somatic cells, whether in vivo or ex vivo, can carry gene addition and editing reagents with distinct therapeutic sequences or specificities depending on the genetic diagnosis. Abbreviations: AAV, adeno-associated virus; CRISPR/Cas9, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/caspase-9; TALEN, transcription activator–like effector nuclease; ZFN, zinc-finger nuclease.
