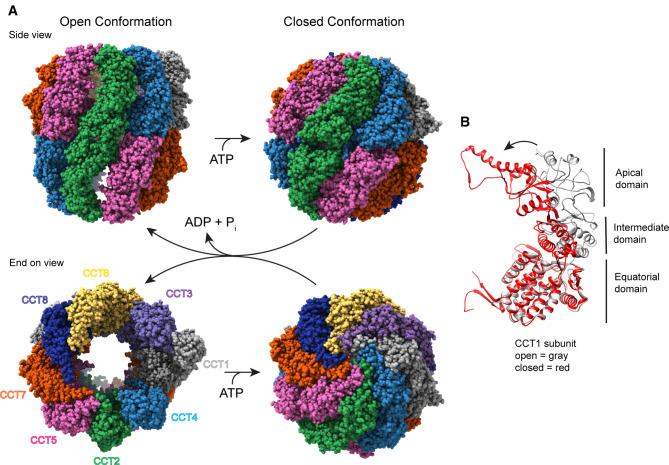
Figure 1. Structure of CCT.
(A) Side and end-on views of human CCT with and without ATP (adapted from PDB 7NVN [32] and 6QB8 [12], respectively), highlighting the double ring arrangement of the eight subunits and the conformational change that occurs in the ATP hydrolysis transition state to cap the central folding chambers of CCT. (B) A ribbon view of the CCT1 subunit showing the domain structure common to all the subunits and the conformational change between the nucleotide-free (gray) and ATP hydrolysis transition state (red) that closes the CCT folding chamber.