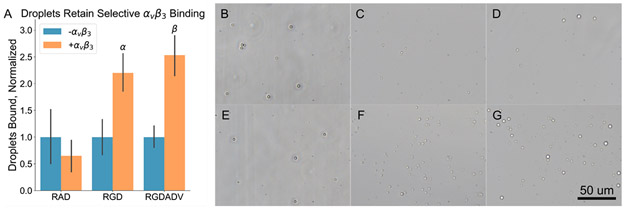
Figure 6.
Droplets retain selective binding capabilities following vaporization and recondensation. (A) A plot of the number of droplets bound within and outside of the αvβ3 coated region, normalized to the number bound outside of the αvβ3 coated region, is shown. No significant differences were observed in the RAD negative control group, indicating that any enhancement of binding efficacy in the two RGD groups was due to specific receptor–ligand interactions. Both control and ADV/RC RGD groups exhibited significantly more droplets bound within the αvβ3 coated region, indicating both groups selectively bound αvβ3. α: p < 0.05, RGD + αvβ3 vs – αvβ3. β: p < 0.05, RGDADV + αvβ3 vs – αvβ3. Representative images of RAD, RGD, and RGDADV groups are shown in the – αvβ3 (B–D) and + αvβ3 (E–F) regions. RGDADV = RGD droplets that underwent ADV/RC.