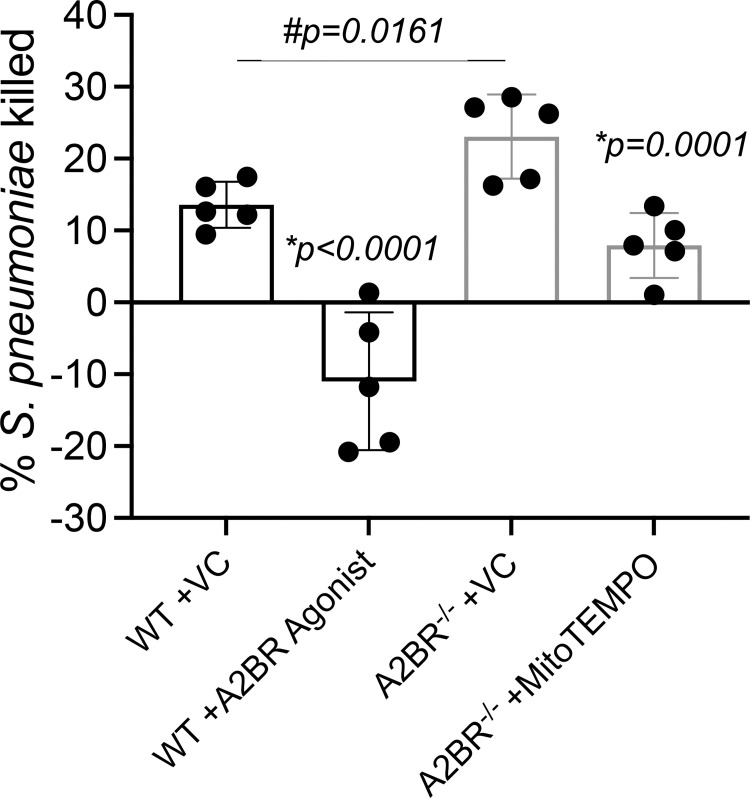
Fig 6. A2B adenosine receptor signaling impairs PMN antibacterial function.
WT (C57BL/6) (black) or A2BR-/- (light grey) bone-marrow derived PMNs were treated with vehicle control (VC), the mitochondrial ROS scavenger MitoTEMPO, or the A2BR agonist BAY 60–6583 and then infected with S. pneumoniae TIGR4. The percentage of bacterial killing was determined with respect to no PMN controls under the same treatment conditions. Data are pooled from n = 5 separate experiments. Bar graphs represent the mean +/-SD. * indicates significant differences from VC treated controls for each mouse strain and # indicates significant differences between indicated VC treated WT vs A2BR-/- groups as measured by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.