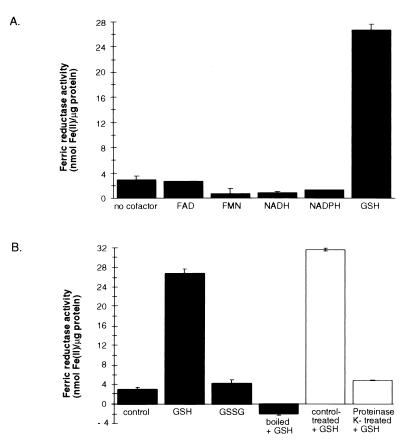
FIG. 4.
Effects of electron donors on ferric reductase activities of high-MW supernatants. (A) Concentraitons of 5 μM FAD, 5 μM FMN, 50 μM NADH, 50 μM NADPH, and 1.63 mM (0.5 mg/ml) GSH were evaluated for the capacity to increase ferric reductase activity. (B) The role of GSH as a specific electron donor for an enzymatic ferric reductase was examined. GSH was added to a high-MW supernatant that was left untreated, boiled for 15 min, or digested with proteinase K. The untreated high-MW supernatant was supplemented with 0.82 mM (0.5 mg/ml) oxidized glutathione (GSSG). Ferric reduction was assayed with Ferrozine as the chromogenic Fe(II) chelator. The averages of triplicate wells from a representative experiment are shown; standard deviations are indicated by bars. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments.