Figure 5.
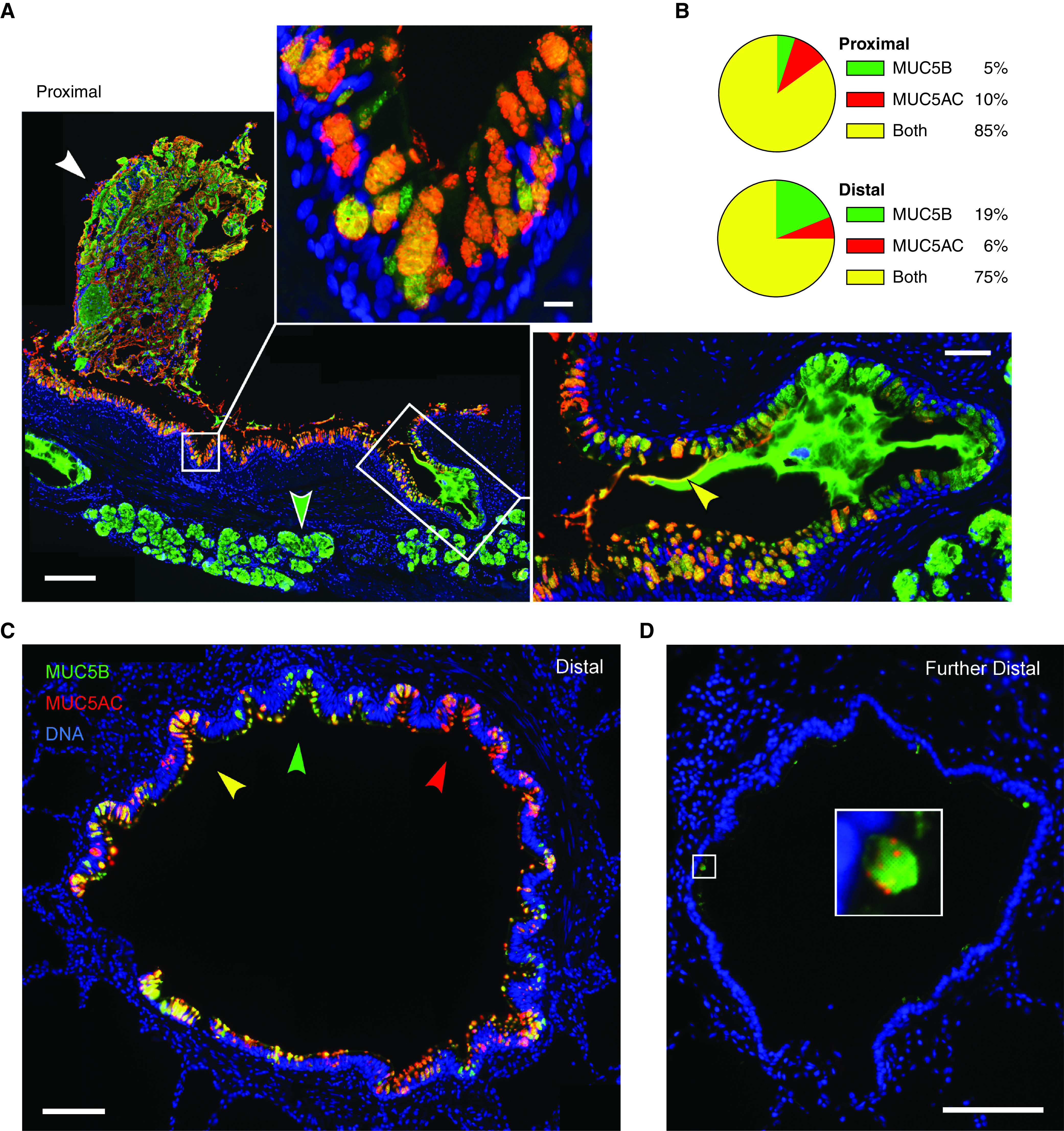
MUC5AC (mucin 5AC, oligomeric gel-forming) and MUC5B (mucin 5B, oligomeric gel-forming) expression in human airways. (A) Representative image of a human proximal airway stained with antibodies against MUC5AC (red) and MUC5B (green), depicting adherent mucus (white arrowhead), surface airway epithelium (top inset), and submucosal glands (green arrowhead and right inset). Scale bar, 200 μm. Top inset shows a higher magnification image of surface airway epithelium; scale bar, 10 μm. Right inset shows a submucosal gland duct opening into the airway with MUC5B-predominant luminal mucus and a thin coating of MUC5AC proximally (yellow arrowhead); scale bar, 50 μm. (B) Pie charts indicate fractions of mucin-containing cells in the proximal and distal airways that have MUC5AC only, MUC5B only, or both mucins. Proximal airways: 1,021 cells, eight subjects; distal airways: 1,687 cells, nine subjects. (C) Distal airway (∼600 μm diameter) depicting furrows with epithelial cells containing predominantly MUC5AC (red arrowhead), MUC5B (green arrowhead), or both (yellow arrowhead). Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) A more distal airway (∼400 μm diameter) containing little intracellular mucin but with scattered cells expressing both mucins. Scale bars: image, 100 μm; inset, 15 μm.
