Figure 7.
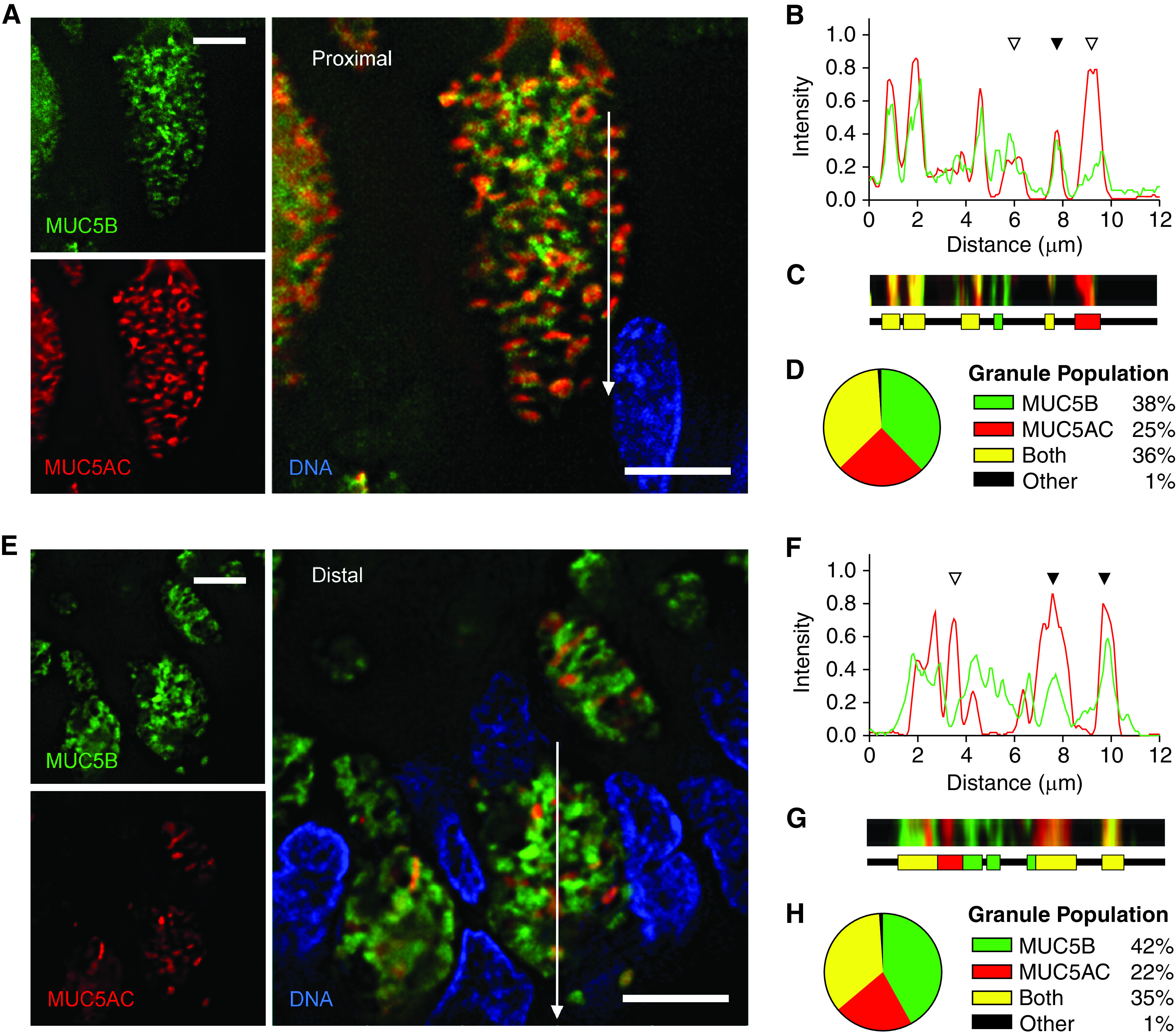
Quantitation of MUC5AC (mucin 5AC, oligomeric gel-forming) and MUC5B (mucin 5B, oligomeric gel-forming) colocalization within granules of human airways. (A and E) Representative deconvolved images of human proximal (A) and distal (E) airways stained with antibodies against MUC5AC (red) and MUC5B (green). White lines indicate the area of measured pixel intensities plotted in B and F. Scale bars, 5 μm. (B and F) Line-scan analyses of pixels in the white lines in A and E are plotted as MUC5AC (red) and MUC5B (green) proportional fluorescence intensity (y-axis) versus the lengths of the white lines (x-axis). Fluorescence intensities were normalized for each image. Correspondence of the peaks for each line indicates colocalization of the mucins (solid triangles), whereas lack of correspondence indicates no colocalization (open triangles). (C and G) Color strips (top) correspond to the white lines but are three pixels wide and smoothed in Photoshop (Adobe) for visibility. Color ribbons (bottom) are generated after discarding the lowest third of pixel intensities in B and F to minimize background noise. Each color segment represents a counted granule. (D and H) Populations of all granules counted in the line-scan analyses. For human proximal airways: 4,988 granules, 360 cells, eight subjects; for human distal airways: 1,138 granules, 106 cells, nine subjects.
