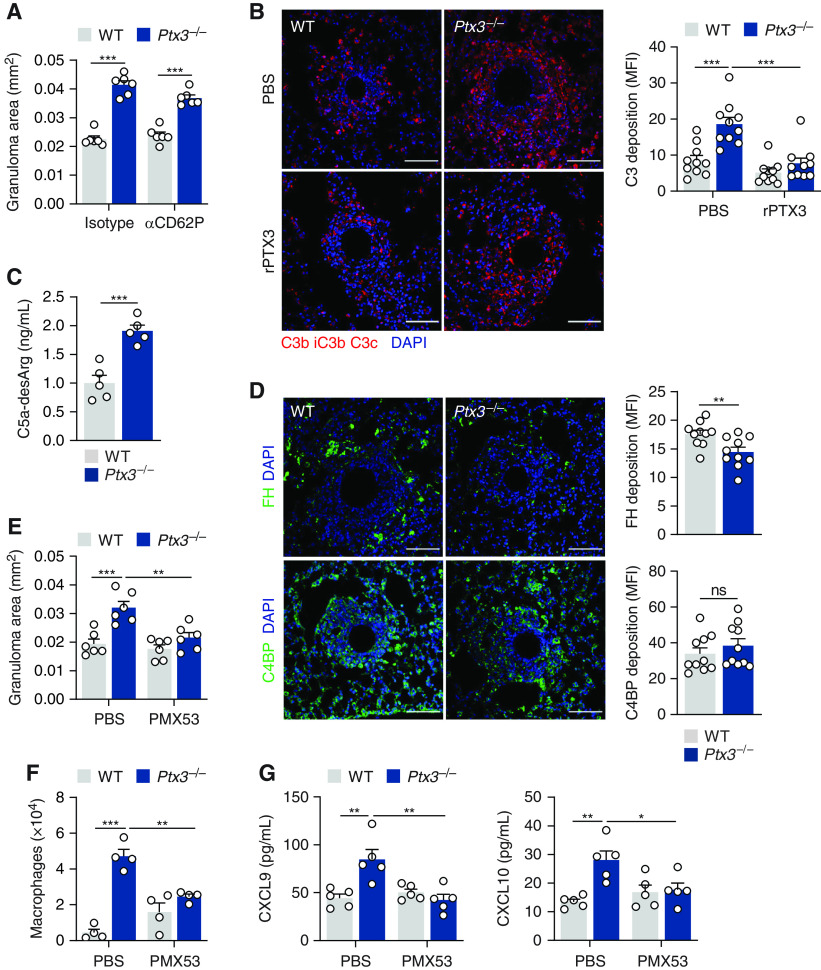
Figure 3.
PTX3 (pentraxin 3) deficiency promotes complement activation during granuloma formation. (A) Area of sodA-elicited granulomas in wild-type (WT) and Ptx3−/− mice on Day 4 after bead embolization and treatment with anti-CD62P or IgG isotype control (n = 6). (B) Immunofluorescence for C3b/iC3b/C3c in granulomas from WT and Ptx3−/− mice on Day 4 after sodA bead embolization and treatment with rPTX3 (recombinant PTX3) or PBS (representative of three independent experiments). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bars indicate 50 µm. Fluorescence was quantified as MFI units. (C) Concentrations of C5a-desArg determined in lung supernatants from WT and Ptx3−/− mice on Day 4 after sodA bead embolization (n = 5). (D) Immunofluorescence for FH (factor H) and C4BP (C4-binding protein) in granulomas from WT and Ptx3−/− mice on Day 4 after sodA bead embolization (representative of three independent experiments). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bars indicate 50 µm. Fluorescence was quantified as MFI units. (E) Area of sodA-elicited granulomas in WT and Ptx3−/− mice on Day 4 after bead embolization and treatment with C5aR1 antagonist PMX53 or PBS (n = 6). (F) The number of alveolar macrophages in the lungs (n = 4) and (G) concentrations of CXCL9 and CXCL10 in lung supernatants (n = 5) from WT and Ptx3−/− mice on Day 4 after sodA bead embolization and treatment with PMX53 or PBS. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001; MFI = mean fluorescence intensity; ns = not significant; PBS = phosphate-buffered saline.