Figure 3.
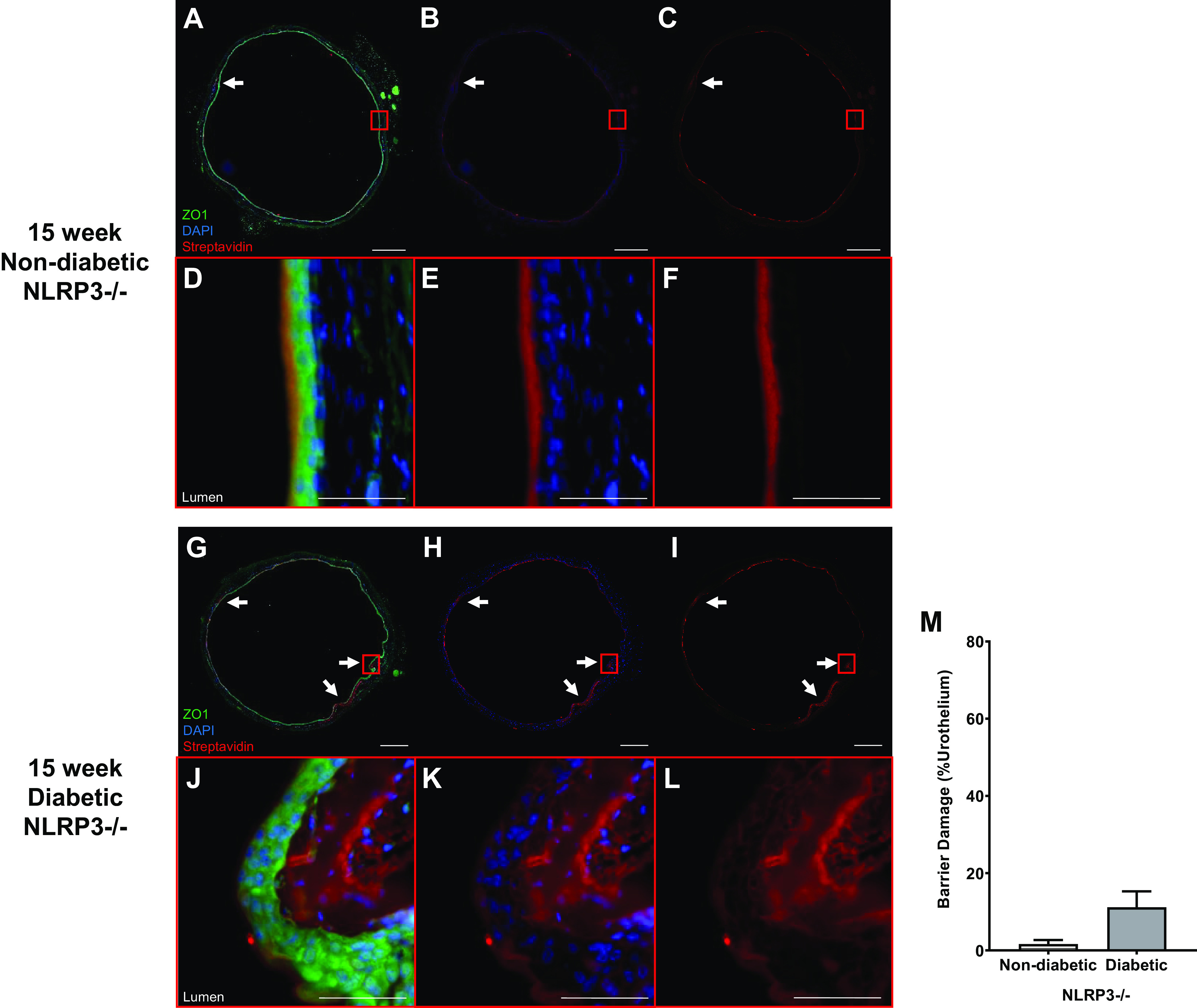
NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) gene deletion prevents diabetes from increasing in vivo urothelial permeability to sulfo-NHS-biotin at the 15-wk (overactive detrusor) time point. Sulfo-NHS-biotin was dissolved in PBS (1 mg/mL) and delivered intravesically (150 μL) through catheters placed in anesthetized mice. The sulfo-NHS-biotin solution was removed after 30 min and replaced with 150 μL of 4% paraformaldehyde. Bladders were tied proximal to ureters, excised, and paraformaldehyde fixed while inflated. Paraffin-embedded sections (5 µm) were then dehydrated and labeled with primary antibody to zona occludens 1 (ZO1) to identify urothelial cells (shown as bright green), Texas red-conjugated streptavidin for sulfo-NHS-biotin detection (red), and DAPI for nuclei (blue). Regions of urothelia (ZO1, green) considered damaged contained sulfo-NHS-biotin (streptavidin, red) in the submucosa. Representative images of bladder sections are shown. White scale bars = 500 μm. The red boxes indicate selected representative regions for magnification. Scale bars inside the red boxes = 50 μm. A–C: 15-wk nondiabetic NLRP3+/+ urothelial barriers were nearly fully intact with sulfo-NHS-biotin staining on the apical surface. Limited regions of damage in which sulfo-NHS-biotin has traversed the urothelia are indicated by white arrows. D–F: representative magnified micrographs of the red boxes in A–C showing that sulfo-NHS-biotin bound to the apical surface without permeating the urothelial layer. G–I: in the absence of NLRP3-mediated inflammation, bladders from 15-wk diabetic NLRP3−/− mice showed few isolated regions of barrier damage indicated by white arrows. J–L: in these magnified images, we found one of those few areas of paracellular sulfo-NHS-biotin staining and submucosal accumulation. Very little urothelial desquamation or single cell pyroptotic deletion was noted. M: overall, NLRP3 gene ablation prevented statistically significant barrier damage in diabetic NLRP3−/− mice. n = 3 and 4 animals, respectively. There were no statistically significant differences (Student’s t test).
