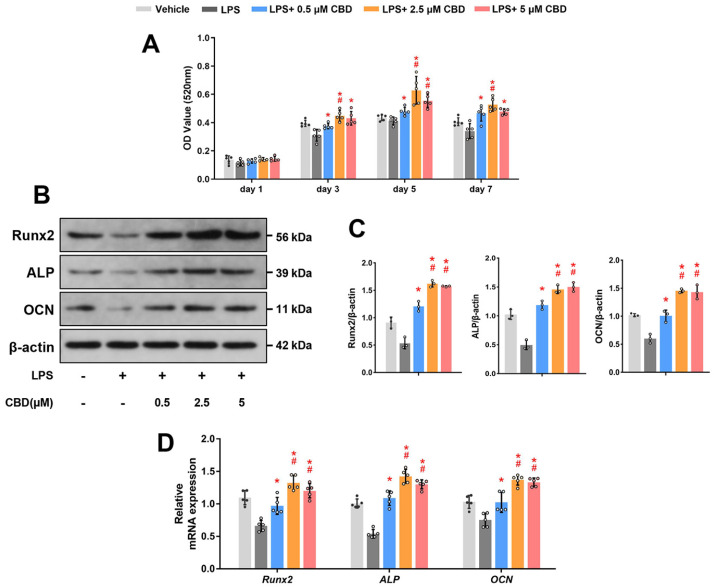
Fig. 3.
CBD promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in the inflammatory microenvironment. (A) BMSCs were co-treated with LPS (10 μg/ml) and different concentrations of CBD (0.5, 2.5, 5 μM), as indicated for 1, 3, 5, and 7 days, then ALP activity was detected (n=5). (B) BMSCs were co-treated with LPS and CBD (0.5, 2.5, 5 μM), as indicated for 7 days. Western blot was performed for detecting Runx2, ALP, and OCN. β-actin was used as the internal control (n=3). (C) Quantitative analysis of (B). (D) BMSCs were co-treated with LPS and CBD (0.5, 2.5, 5 μM), as indicated for 7 days. Then, BMSCs were harvested for detecting the mRNA expression levels of Runx2, ALP, and OCN by qRT-PCR. β-actin was used as the internal control (n=5). CBD: cannabidiol, BMSCs: bone mesenchymal stem cells, Runx2: runt-related transcription factor 2, ALP: alkaline phosphatase, OCN: osteocalcin, qRT-PCR: quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Data are represented as means±SD. *p<0.05 compared with the LPS group; #p<0.05 compared with the LPS plus 0.5 μM CBD group.