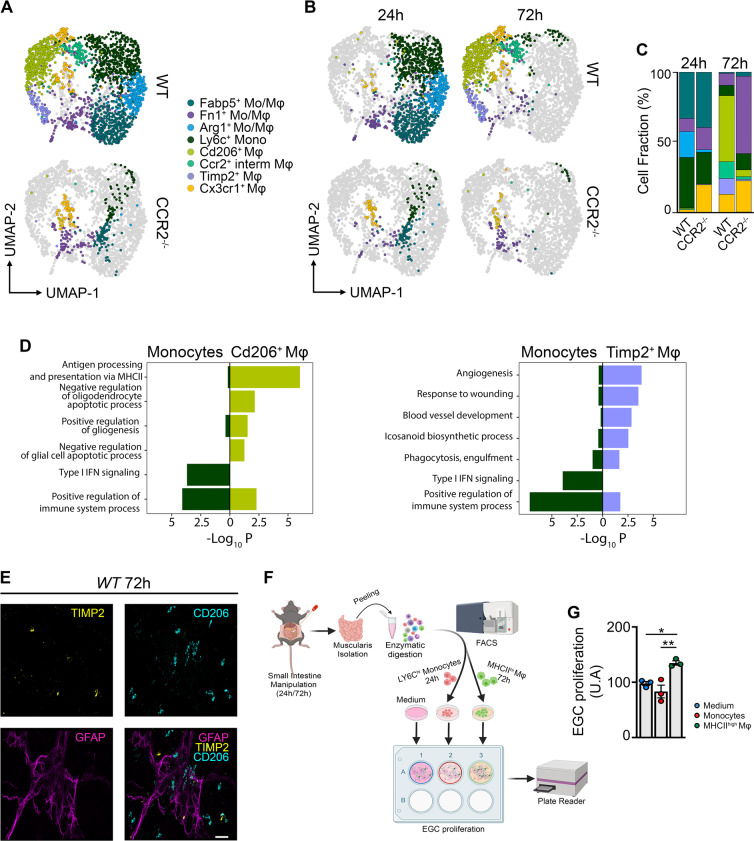
Fig. 3. Two distinct Mφ subpopulations during the resolution of muscularis inflammation are derived from CCR2+ monocytes.
a UMAP of monocyte and Mφ subclusters from the muscularis of WT and CCR2−/− mice at 24 h and 72 h after induction of muscularis inflammation. Each sample was pooled from 3–4 mice. b UMAPs of myeloid cells at different time points post-injury. c Cell fraction of each subcluster relative to the total number of myeloid cells at different time points after muscularis inflammation. d GO analysis of monocytes versus Cd206+ Mφs (left) or Timp2+ Mφs (right) showing negative Log10(p-value). e Immunofluorescent images of muscularis whole-mount preparations 3 days after the induction of muscularis inflammation stained for GFAP (purple), TIMP2 (yellow) and CD206 (light blue). Scale bar 15 µm. f Experimental outline of in vitro EGC proliferation by stimulation with supernatant of monocytes or Mφs from different time points post-injury. g Fold induction of EGCs stimulated with the supernatant of LY6Chi monocytes from 24 h post-injury or MHCIIhi Mφs from 72 h post-injury relative to control medium. Every data point is an independent sorting and culture experiment One-way ANOVA; test *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ns not significant.