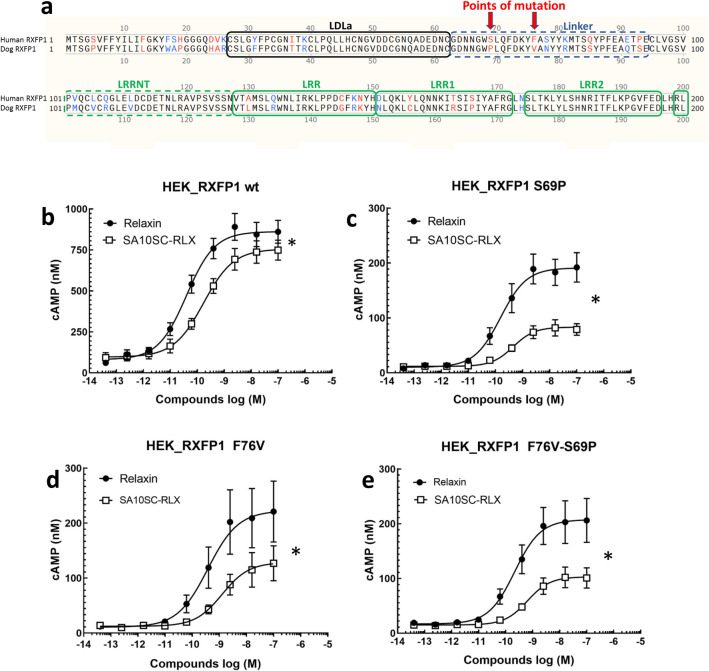
Figure 3.
Role of linker domain in RXFP1 activation by SA10SC-RLX. Alignment of human RXFP1 (protein sequence NP_067647.2) with dog RXFP1 (sequence MW713050) across the first 200 amino acids of the N-terminus showing the LDLa and linker domains The arrows indicate the point mutations of interest (S69P and F76V) in the linker domain between the LDLa domain and the first LRR domain of the extracellular domain of RXFP1 (a). Concentration dependent effects of relaxin and SA10SC-RLX on cAMP production in HEK_RXFP1 cells (mean ± SEM, n = 4 experiments performed in duplicate) (b). Significantly decreased response of SA10SC-RLX compared to relaxin on cAMP production in HEK_RXFP1 cells mutated in the linker in position S69P (c), F76V RXFP1 (d) or F76V-S69P (e) (mean ± SEM, n = 4 experiments performed in duplicate). For Emax comparison between relaxin and SA10SC-RLX, normality hypothesis was confirmed for each group and a paired T test was performed. In the absence of normality hypothesis, a Wilcoxon test was performed (*P < 0.05).