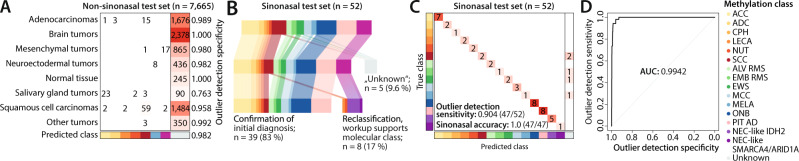
Fig. 5. Classifier development and application to an independent test set.
A Confusion matrix of the non-sinonasal samples from the test set, split up in different categories. Overall, the classifier achieved a specificity of 0.982, ranging from 0.763 in salivary gland tumors to 1.0 in normal tissue and brain tumors. B Overview of the classification results from the test set. Out of 52 samples, five cases were assigned to the Unknown class, resulting in an outlier detection sensitivity of 0.904. Out of the 47 remaining specimens, DNA methylation-based classification confirmed the initial diagnosis in 39 samples (83%). Eight specimens (17%) were reclassified to a divergent DNA methylation class. Additional molecular workup supported the DNA methylation-based reclassification in all cases. C Confusion matrix from the sinonasal test set shows an accuracy of 1.0 for classification of sinonasal tumors. D Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of the support vector machine classifier with regards to the binary outlier detection problem with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.9942.