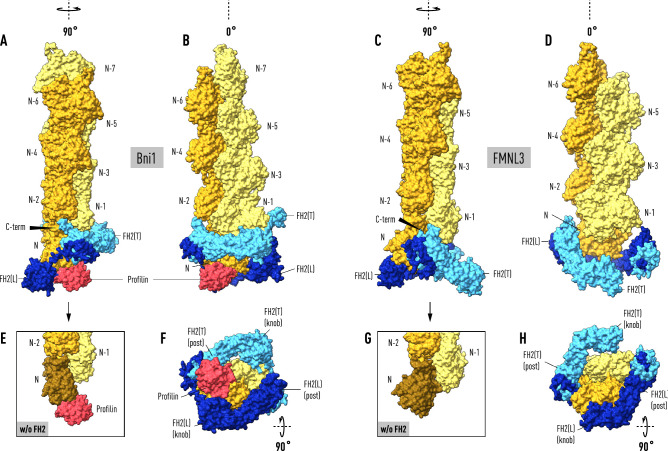
Figure 1.
Actin filaments docked onto formin:actin heterodimers support a ‘stepping second’ model. The two panels on the left depict the result of superimposing the terminal subunit of a 6-mer (in lemon and orange) of the helical actin filament (PDB code: 6DJO) onto actin molecule (N−1) bound to the trailing FH2(T) domain (light blue) in the Bni1:actin heterodimer (PDB code: I64Y). With this alignment, actin(N) bound to FH2(L) (in dark blue) does not fit the helical symmetry of the filament but is instead coplanar with actin(N−2). Actin subunits in the filament are not N-acetylated. Superposing β-actin from the crystal structure of profilin-β-actin (PDB code: 2BTF) onto actin(N) places profilin (in red) in a shallow surface pocket where it forms significant salt-bridges with FH2(L) and the N-terminus of actin(N). The coplanarity of actin(N) (in brown) with actin(N−2) is seen in the bottom panels (E,G) where FH2 has been removed. The two panels on the upper right show the terminal subunit of a 6-mer of the helical actin filament docked onto actin(N) of the mammalian formin FMNL3:actin crystal structure (PDP code: 4EAH). For consistency in relating the Bni1 and FMNL3 filament-bound structures to a second stepping model, the FH2 domains are labeled so that actin(N) is bound to FH2(L) on the right even though it is not the ‘leading’ FH2 domain. Not shown in the panels on the right is the actin molecule bound to FH2(T) in the crystal structure which is in a ‘jammed’ position evidently caused by front-to-back packing between the two ‘biological units’ in the asymmetric unit (see “Methods”). Alignment of the filament axes in the Bni1 (left panels) and FMNL3 models (right panels), discloses a two-state ‘stepping second’ model in which FH2(T) descends towards the barbed end to create an open pocket for the binding of actin(N+1) with the dissociation of profilin from actin(N). The arrows (panels A and C) point to the prominent α-helix at the C-terminus (C-term) of FH2(T) at the interface between actin(N−2) and actin(N).