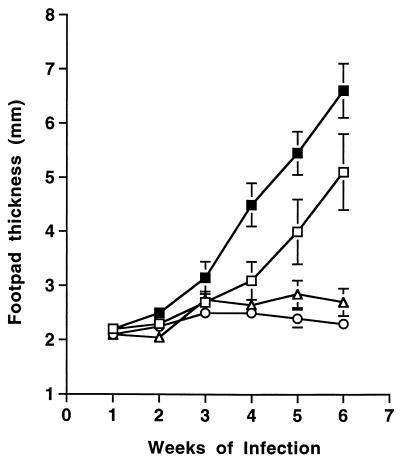
FIG. 1.
Treatment with anti-CTLA4 MAb accelerates the progression of cutaneous leishmaniasis in normally susceptible BALB/c mice but does not affect the outcome of disease in normally resistant C57BL/6 mice. Groups of five infected BALB/c mice were injected intraperitoneally on days 0 and 7 of infection with 0.3 mg of rat IgG (□) or anti-CTLA4 MAb (■). Groups of five C57BL/6 mice were similarly treated with rat IgG (○) and anti-CTLA4 MAb (▵). Shown are the mean and standard error of the mean for footpad thicknesses measured at weekly intervals after injection of 2 × 106 L. major promastigotes into both hind feet. Differences in footpad size for BALB/c mice were statistically significant (P < 0.05) from week 3 onward, whereas differences in C57BL/6 footpad sizes were not significantly different.