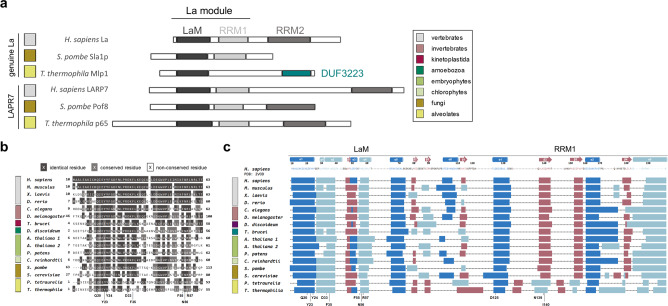
Fig. 1. Alveolate La proteins are predicted to have a LaM but not an RRM1.
a Schematic representation of RNA-binding domains found in La and La-related protein-7 (LARP7) from different eukaryotes. The LaM and RRM1 together form the La module responsible for uridylate binding through formation of a hydrophobic binding pocket between the two domains. LaM La motif, RRM RNA-recognition motif, DUF domain of the unknown function. b Primary amino acid sequence alignments from different eukaryotic lineages showing conservation of uridylate binding residues (highlighted, bottom). A dark gray background indicates identical residues, light gray conserved residues, and white indicates no conservation. Color-coded legend is shown in (a). Full LaM and RRM1 domains are shown in Supplementary Fig. S1a, b. c Secondary structure predictions of LaM and RRM1 from different eukaryotic lineages. Predicted β-sheets shown in red and predicted α-helices in blue (dark blue: typical α-helices found in the winged-helix fold and classic RRM, light blue: inserted α-helices found in La proteins specifically) are compared against the secondary structure motif of the hLa protein crystal structure on the top (PDB: 2VOD). The location of the conserved amino acid residues important for uridylate binding are shown at the bottom. Color-coded legend is shown in (a).