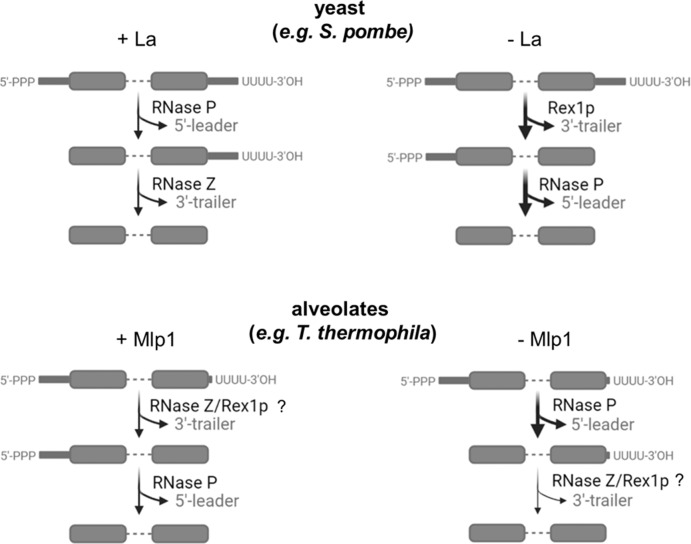
Fig. 7. Model for pre-tRNA processing in T. thermophila.
During La-dependent processing (top, left) in previously studied eukaryotes such as yeast, the La protein is the first protein to associate with pre-tRNAs on the 3’-stretch of uridylates generated by RNA polymerase III transcription termination. Binding of La provides protection from degradation by 3’-exonucleases, assists with tRNA folding through RNA chaperone activity and stabilizes the nascent pre-tRNA. The next step in tRNA processing is endonucleolytic removal of the 5’-leader by RNase P, followed by an endonucleolytic cut by RNase Z resulting in removal of the 3-trailer sequence and the La protein bound to the uridylate stretch. In contrast, during La-independent processing of pre-tRNAs (top, right), the 3’-trailer is rapidly removed first by 3’-exonucleases such as Rex1p, followed by RNase P processing resulting in an end-matured tRNA. Our data from T. thermophila point towards a pre-tRNA processing model in which Mlp1-dependent processing (bottom, left) 3’-trailers are processed efficiently. Mlp1-independent processing results in the accumulation of pre-tRNAs containing unprocessed 3’-trailer sequences, indicating that Mlp1 is required for efficient 3’-end processing unlike other eukaryotes. Image created with BioRender.com. The Publication License is provided as a Source Data file.