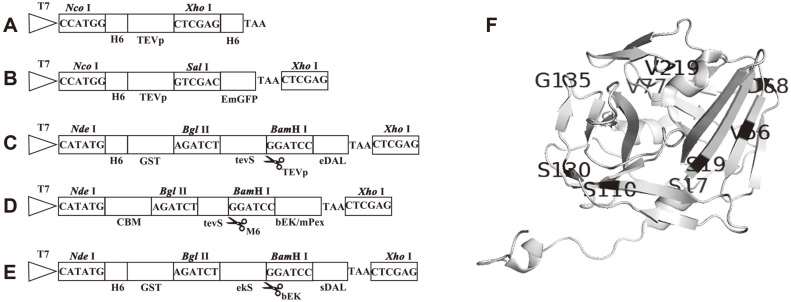
Fig. 1. Design of fusion proteins.
All target genes were cloned in frame downstream of the PT7lac promoter in the pET expression plasmids. The restriction enzymes are indicated above the genes, and the fusion constructs were schematically represented below the genes (not to scale). (A) The double His6-tagged TEVp5M contains T17S, L56V, N68D, I77V, S135G, and S219V. Each and combined C19S, C110S and C130S were introduced into the TEVp5M, respectively. (B) The constructed TEVp was fused to the EmGFP for detecting production level in soluble extracts. (C) The His6-GST tagged eDAL for the TEVp cleavage. Between the His6-GST and eDAL, the tevS representing as the ENLYFQ↓G encoded by the sequence including BglII and BamHI cut sites was incorporated. (D) The sequence encoding the CBM-tagged bEK or mPex. The tevS was introduced between two protein partners. After refolding, the fusion protein was cleaved by the M6 variant for releasing the target protein. (E) The His6-GST tagged sDAL as the bEK substrate. As shown in Fig. 1C, the placed tevS was substituted with the ekS. (F) The mutational amino acids in the TEVp are based on the crystal structure (Protein Data Bank code 1LVM). The figure was created with the program Pymol (https:pymol.org).