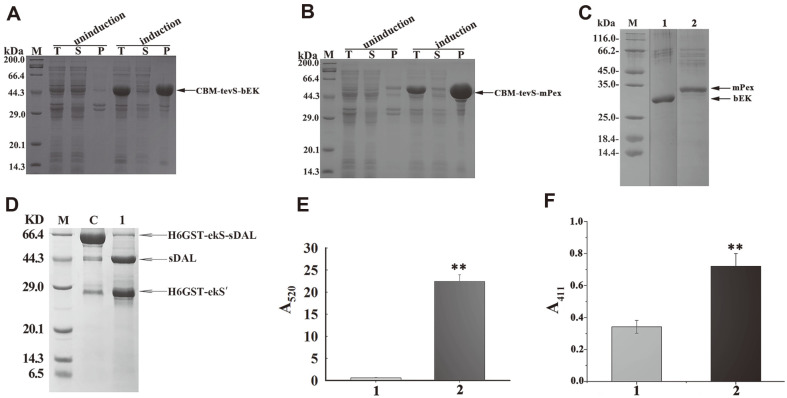
Fig. 6. Overexpression, refolding, tag removal, and activity assay of the disulfide-bonded bEK and mPex.
A: SDS-PAGE analysis of the CBM-tagged bEK produced in E. coli BL21(DE3) strain. T: total protein. S: soluble fraction. P: insoluble fraction. B: SDS-PAGE analysis of the CBM-tagged mPex. C: the refolded tag-free bEK and mPex released from RAC resin with the purified M6 incubation. Lane 1: the refolded tag-free bEK. Lane 2: the refolded tag-free mPex. Arrows indicate the two purified enzymes. D: Cleavage of purified His6-tagged GST-ekS-sDAL with the refolded bEK. Lane C: the fusion protein incubated with the heat-inactive bEK. Lane 2: the fusion protein incubated with the refolded tag-free bEK. Arrows indicate fusion protein substrate and cleaved products. The His6-tagged GST fused to partial ekS as the cleaved product was denoted as H6GST-ekS’. E: The coupled assay of the refolded tag-free bEK activity. Absorption from the mixture in the absence and presence of the refolded tag-free bEK is indicated as light and dark grey columns. F: Activity of the mPex catalyzing 10 mM H2O2 degradation. Absorption from the mixture in the absence and presence of the refolded tag-free mPex is indicated as light grey and black columns. The asterisk indicates significant differences higher than the inactivated enzyme as the control; *p < 0.01.