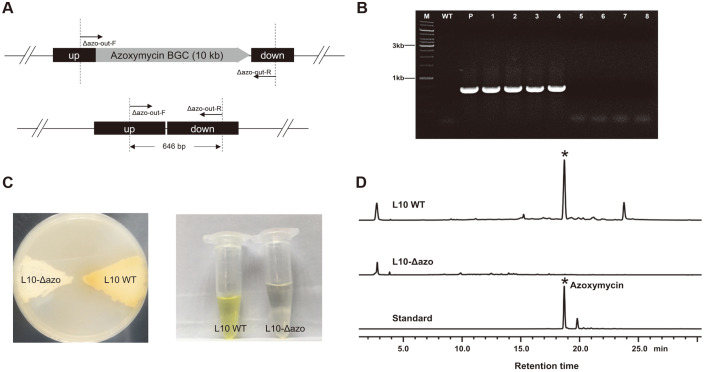
Fig. 3. Deletion of the azoxymycin BGC in S. chattanoogensis L10.
(A) The schematic diagram of the doublecrossover mutants. Up, the upstream homologous arm of azoxymycin BGC; while down, the downstream homologous arm of azoxymycin BGC. The primer pair Δazo-out-F/Δazo-out-R was used for PCR verification. (B) PCR verification of the L10- Δazo mutants. Lane M, DNA marker; lane WT, wild-type S. chattanoogensis L10; lane P, pSUC02; lane 1-4, double-crossover mutants (4 colonies that secreted no yellow azoxymycin into the plate); lane 5-8, reverted wild-type colonies (4 randomly selected colonies that secreted yellow azoxymycin into the plate). (C) Color comparisons of substrate mycelia and fermentation broth extract between the L10-Δazo mutant and L10 WT strain. The strains were cultured for 5 days on the YMG agar plate before being photographed. (D) The HPLC analysis of the fermentation broths at 120 h.