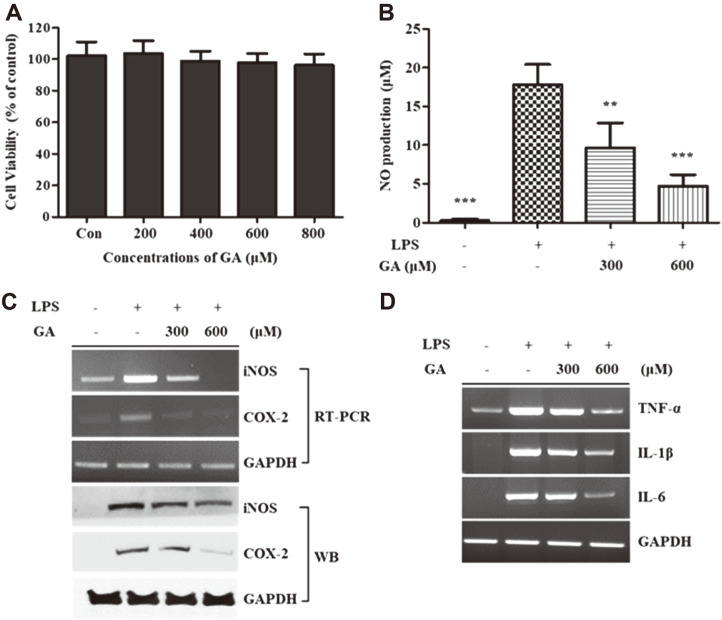
Fig. 1. Effects of GA treatment on cell viability and inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 cells.
(A) RAW 264.7 cells were incubated with and without GA (200, 400, 600, and 800 μM) for 24 h. Cell viability was measured using WST-1 assays. (B–D) RAW 264.7 cells were pre-incubated with GA (300 and 600 μM) for 2 h and then stimulated using LPS treatment for 22 h. Supernatants were harvested, and the production of NO was determined using the Griess reagent. The mRNA and protein expression levels of iNOS and COX-2 from whole-cell lysates were measured using RT-PCR and WB, respectively. The mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in whole cells were measured using RT-PCR. Data in the graph are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. the LPS-stimulated group. GAPDH was used as a loading control. GA, gentisic acid; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL, interleukin; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; WB, western blotting.