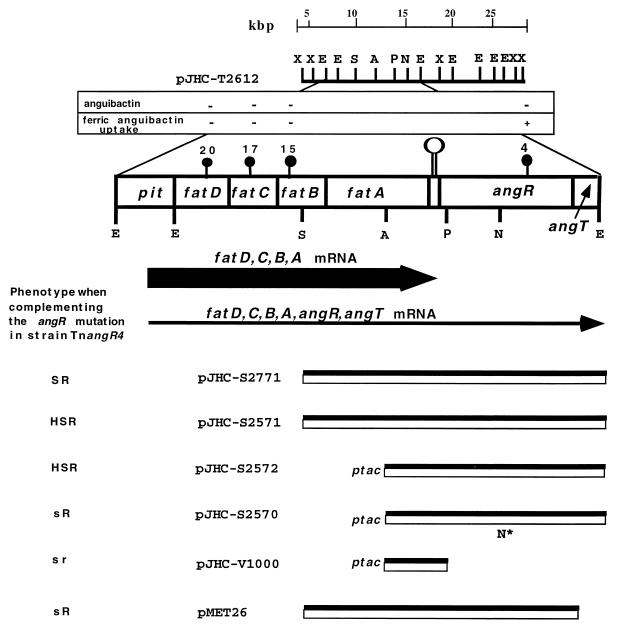
FIG. 1.
Genetic and physical map of plasmids used in this study. The dark circles symbolize the Tn3::HoHo1 transposon insertion mutants 20, 17, 15, and 4 in pJHC-T2612. The Tn3::HoHo1 transposon is approximately 14 kb and carries the ampicillin resistance marker in addition to a promoterless lacZ (52). Restriction sites are as follows: X, XhoI; E, EcoRI; S, SalI; A, AvaI; P, PstI; B, BamHI; N*, NcoI-site modified with the Klenow fragment of DNA polymerase I. The insert DNA from pJM1 is represented by the double black and white boxes. The vector DNA is not represented. pJHC-T2612 contains the iron uptake region of pJM1 cloned in the pVK102 vector. pJHC-S2771 and pMET26 are subclones carrying the angR gene from plasmid pJM1 cloned in pJHC-S100, a pBR325 derivative (see Table 1). pMET26 is an isogenic construct with pJHC-S2771 except that angT has been deleted. pJHC-2571 harbors the angR gene from pJHC1 also cloned in pJHC-S100. Plasmid pJHC-S2572 carries the angR gene from pJHC1 under the control of the ptac promoter by using the cloning vector pKK-223-3. Plasmid pJHC-2570 is an NcoI modification in the angR gene of pJHC-S2572, and pJHC-V1000 is a deletion at the PstI site within the angR gene, obtained from pJHC-2572. Pit is the promoter for the iron transport genes (11). The thick horizontal arrow represents the most abundant polycistronic transcript (fatDCBA mRNA) that terminates at or adjacent to the hairpin (open lollipop shape) located between the end of fatA and the beginning of angR. This hairpin has the characteristics of a rho-dependent transcription termination signal (2). The thin horizontal arrow represents a low-abundance polycistronic transcript (fatDCBA, angR, and angT mRNA). Phenotypes of the complementing plasmids in strain TnangR4 are as follows: HS, high siderophore production (531A-type); S, normal siderophore production (775-type); s, low or no siderophore production; R, positive for iron transport gene regulation; r, reduced or no iron transport gene regulation.