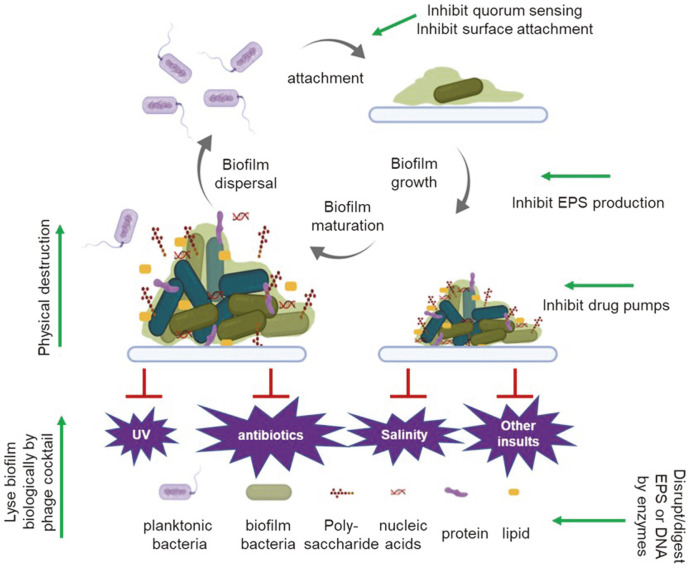
Fig. 1. Structure and life cycle of bacterial biofilms.
(1) Initial surface attachment of planktonic bacteria cells; (2) cell to cell adhesion and biofilm growth; (3) biofilm maturation; and (4) cell detachment and biofilm dispersal. Polysaccharides, nucleic acids, protein and lipids are major components of biofilms. The biofilm form of bacteria is resistant to many environmental insults, including UV light, antibiotics, and salinity. Anti-biofilm methods mentioned in this review are shown, indicated with green arrows at the locations where they act.