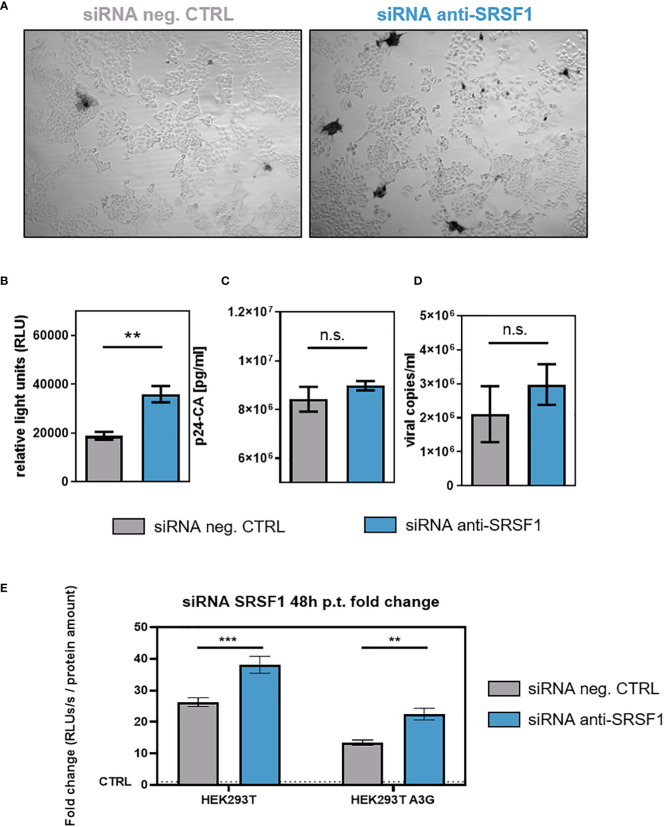
Figure 8.
Impact of siRNA-based knockdown of SRSF1 on HIV-1 infectivity and virus production. RPE-ISRE luc cells were transfected with a plasmid coding for the proviral clone NL4-3 (AD8) (pNL4-3 AD8) and the indicated siRNA. Seventy-two hours post-transfection, cellular supernatant was harvested. (A, B) Viral infectivity was determined via TZM-bl assay. (A) Infected TZM-bl cells were stained with X-Gal. (B) Luciferase activity was determined measuring relative light units (RLUs). (C) p24-CA ELISA was performed to determine p24-CA levels in the cellular supernatant. (D) Cellular supernatant was used to determine viral copy number per milliliter. RT-qPCR was performed analyzing absolute expression levels of exon 7-containing transcripts (total viral mRNA). Statistical significance was determined using unpaired two-tailed t-tests (**p < 0.01). Mean ( ± SEM) of n = 4 biological replicates is shown for (B), (C), and (D). (E) HEK293T- and HEK293T APOBEC3G-expressing cells were seeded in poly-L-lysine (Sigma-Aldrich) pre-coated wells. Cells were transiently transfected with the proviral clone pNL4-3 and 12.8 nM of the indicated siRNA. Supernatants were harvested 48 h post-transfection and applied to TZM-bl cells. Forty-eight hours post-infection, cells were lysed for luciferase assay. The RLUs/s were normalized to whole protein amounts as determined using Bradford assay. The fold change is normalized to the signal of uninfected TZM-bl cells. Mean ( ± SEM) of n = 4 biological replicates and n = 2 technical replicates is shown. The significance was analyzed using two-way ANOVA (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ns, not significant).