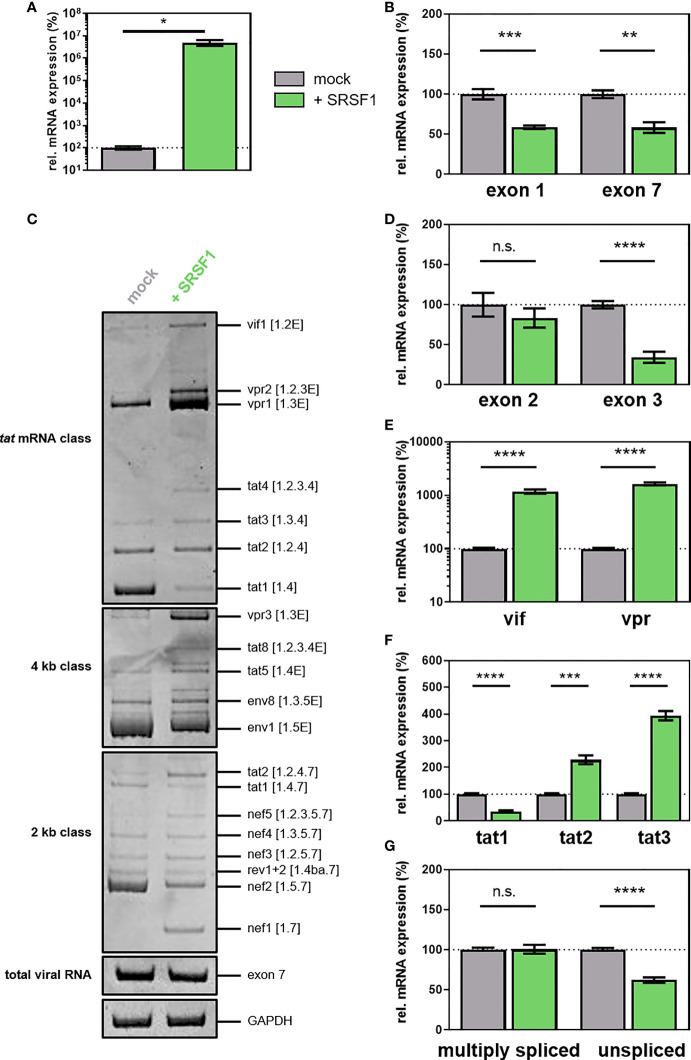
Figure 9.
(A–G) Overexpression of SRSF1 affects HIV-1 LTR transcription and alternative splice site usage. HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with a plasmid coding for the proviral clone NL4-3 PI952 (pNL4-3 PI952) and a plasmid expressing FLAG-tagged SRSF1 (pcDNA-FLAG-SF2) or an empty vector [pcDNA3.1(+)] as mock control. Cellular RNA and cell culture supernatant were harvested 72 h post-transfection and subjected to further analysis. (A, B) RT-qPCR was performed to determine relative mRNA expression levels of (A) SRSF1 and (B) exon 1- and exon 7-containing mRNAs (total viral mRNA). GAPDH was used for normalization. (C) RT-PCR was performed using the indicated primer pairs covering the viral mRNA isoforms of the 2-kb, 4-kb, and tat mRNA class ( Supplementary Tables 1 , 2 and Supplementary Figure 4 ). HIV-1 transcript isoforms are indicated according to Purcell and Martin (36). HIV-1 exon 7-containing transcripts as well as cellular GAPDH were included as loading controls. PCR amplicons were separated on a 12% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel. (D, G) Total RNA was subjected to RT-qPCR to measure relative mRNA expression levels of (D) exon 2- and exon 3-containing, (E) vif and vpr, (F) tat1, tat2, and tat3, and (G) multiply spliced and unspliced mRNAs using the indicated primers. Relative viral splice site usage was normalized to exon 7-containing mRNAs (total viral RNA). Unpaired two-tailed t-tests were used to calculate statistical significance (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001). Mean ( ± SEM) of n = 4 biological replicates is depicted for (A, B) and (D–G). For (C), a representative gel is shown. ns is not significant.