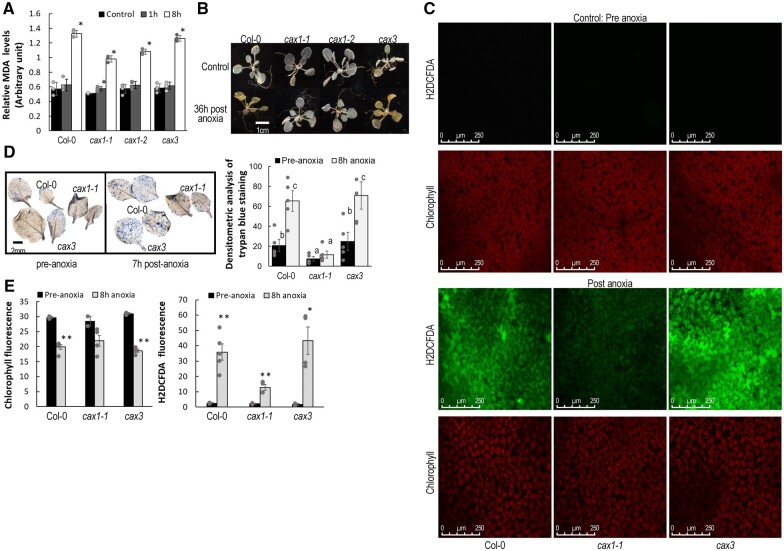
Figure 4.
Effect of mutations in CAX genes on post-anoxia production of reactive oxygen species. A, Col-0 and cax3 displayed higher induction of lipid peroxidation as measured by MDA. Plants belonging to nine-rosette leaf stage were treated as described in Figure 1B and aerial portions of the plants were sampled 1 h and 8 after returning to normoxia conditions. Plants sampled prior to the anoxic conditions were used as controls. All results are means ± sem, n = 3. Asterisk indicate significant differences compared to pre-anoxia conditions at P < 0.01, as calculated from Student’s t test in Excel. B, Reduced H2O2 in cax1 compared to Col-0 and cax3 when recovering from anoxia as measured via DAB staining. A dark brown precipitate indicates the presence of H2O2. Whole rosettes from 3-week-old plants were exposed to anoxic conditions for 7 h. Rosettes were sampled 36 h after the plants were brought back to normoxia growth conditions. Unstressed plants were used as the control. Although there is variability among plants of the same genotype, the results were consistent. These data are representative of more than three independent experiments. C, Col-0 and cax3 plants demonstrated elevated H2O2 fluorescence using the cell permeable dye H2DCFDA in rosette leaves post anoxia compared to cax1. In the presence of ROS, H2DCF is oxidized to DCF, giving the fluorescence in Col-0 and cax3. Three-week-old plants were exposed to anoxic conditions for 8 h in dark. Following anoxia stress, mature whole rosette leaves were detached from the plants and were used for staining, Scale bar = 250 µM. Fluorescence signals quantified by ImageJ are given in the lower panel. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to pre-anoxic conditions using Student’s t test in Excel (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.005). Although there is variability among plants, the trends were consistent. Data are a representative three independent experiments and error bars indicate standard error of the mean. D, Cell death in leaves as measured by trypan blue staining was higher in Col-0 and cax3 post anoxia compared to cax1. Plants belonging to nine-rosette leaf stage were subject to anoxia as described in Figure 1A and leaves were sampled 7 h after the plants were returned to normoxia. Nine leaves were used to quantify the cell death intensity. The letters indicate that there is a statistically significant difference between two columns (level of significance 95%) as calculated from Student’s t test in Excel. Error bars indicate standard error from mean.