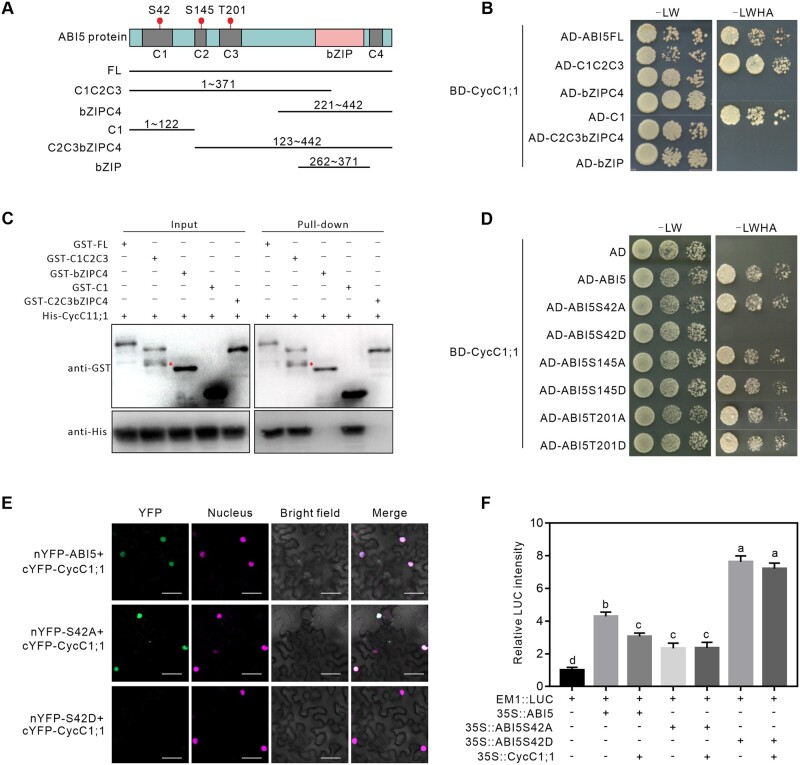
Figure 7.
ABI5 Ser-42 phosphoamino acid affects ABI5 interaction with CycC1;1. A and B, Identification of the CycC1;1-interacting domain of ABI5 via Y2H assay. The diagram in the box (A) indicates the conserved domains in ABI5 and the truncated fragments tested in the assays. The full-length and truncated ABI5 proteins were fused to the AD of GAL4, and CycC1;1 was fused to the BD of GAL4. Protein interactions were examined based on the growth of yeast cells on selective media (B). C, GST pull-down assay to analyze the CycC1;1-interacting domain of ABI5. 6×His-CycC1;1 were mixed with GST-tagged full-length or truncated ABI5 proteins and then immobilized on glutathione sepharose beads. After washing, the eluted proteins were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-GST and anti-His antibodies, respectively. D, Y2H assay to analyze the interaction between CycC1;1 and phospho-mimic or phospho-dead forms of ABI5 at the Ser42, Ser145, and Thr201 sites. E, BiFC analysis to examine the interaction between CycC1;1 and ABI5, ABI5S42A or ABI5S42D in N. benthamiana leaves. Scale bars = 20 μm. F, Dual-LUC reporter gene assay to examine the effects of ABI5, ABI5S42A, or ABI5S42D on EM1 expression in the presence or absence of CycC1;1. The activity of EM1::LUC alone was set to 1. Error bars indicate mean ± sd (n = 3). Different letters indicate significant differences as determined using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (P < 0.05).