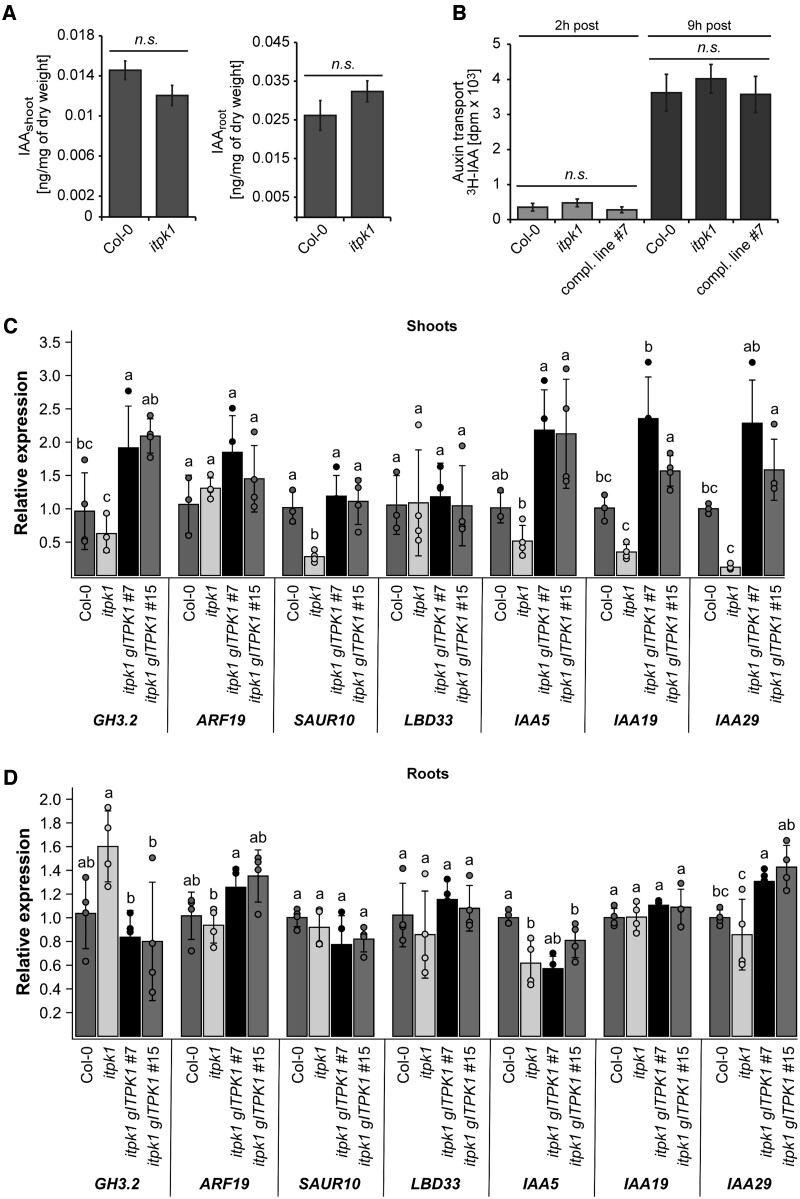
Figure 4.
Arabidopsis itpk1 plants are not defective in auxin synthesis and transport but are compromised in auxin-related gene expression. A, Auxin (IAA) levels in shoot and roots of 2-week-old seedlings of designated genotypes grown on solidified half-strength MS media, supplemented with 1% (w/v) sucrose. Error bars represent sem (n ≥ 7, biological replicates). The experiment was repeated with similar results. Statistical significance was determined by two-tailed Student’s t test (P < 0.01). Differences between the designated genotypes were not significant (n.s.) as indicated. B, Polar auxin transport. The apical end of excised stems of designated genotypes were placed in liquid solidified half-strength MS media, supplemented with 1% (w/v) sucrose and [3H] IAA. After indicated times of incubation, the basal ends of the labelled stems were excised, and the activity was determined by scintillation counting. Error bars represent sem (n = 3, biological replicates). Statistical significance was determined by two-tailed Student’s t test (P < 0.01). Genotypes in all panels are as indicated. Differences between the designated genotypes were not significant (n.s.) as indicated. C and D, Relative expression of auxin-responsive genes in shoot (C) and root (D) of wild-type (Col-0), itpk1 mutant and two selected complemented lines, determined by RT–qPCR analyses using RNA extracted from 2-week-old seedlings grown on solidified half-strength MS media, supplemented with 1% (w/v) sucrose. Βeta-TUBULIN served as a reference gene. Shown are means ± sd (n = 3 or 4). Letters indicate significant differences between the lines in each gene by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s HSD test (P < 0.05).