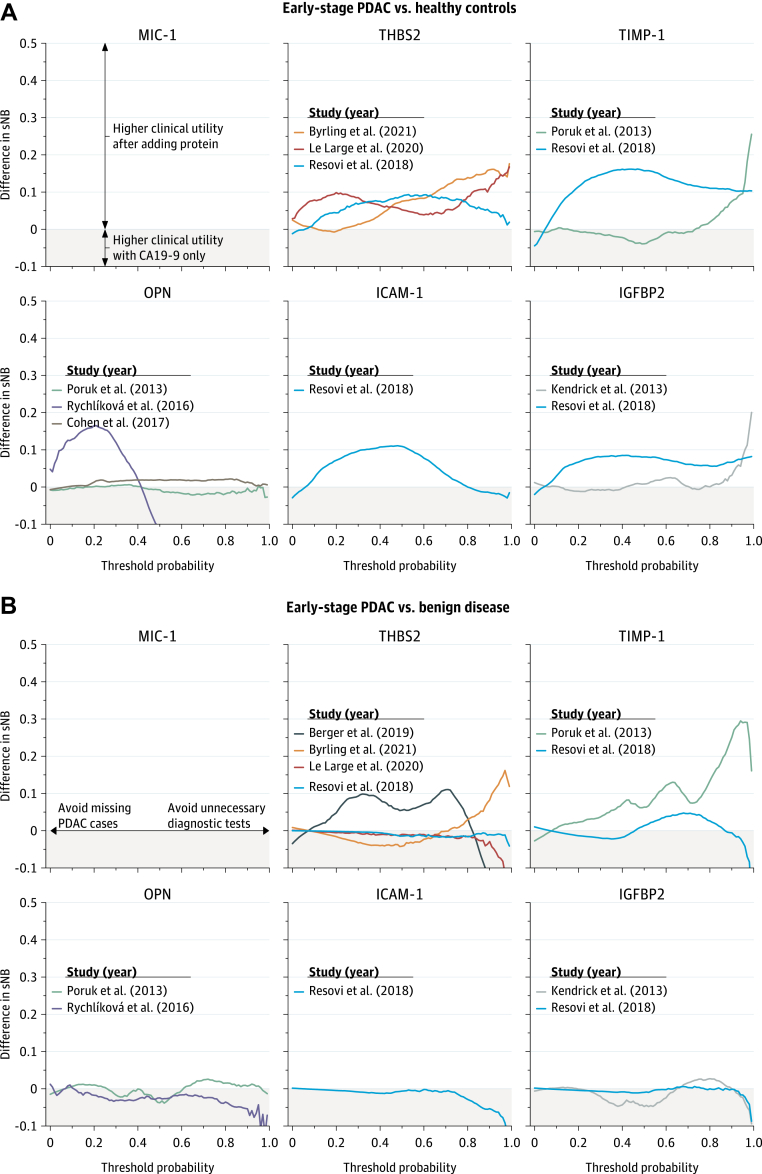
Fig. 5.
Incremental clinical utility of protein biomarkers in individual studies. PDAC indicates pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; sNB, standardized net benefit. The sNB can have negative values (clinical harm), and typically ranges between 0 (no clinical utility) and 1 (maximum clinical utility). The threshold probability of disease indicates the minimum risk of disease a patient needs to have before certain interventions are considered. For instance, if a clinician performs 100 biopsies to find 20 PDAC cases, then the threshold probability is 20%, and the benefit of detecting one PDAC case is deemed to be ([100-20]/20=) 4 times higher than the harm of performing one unnecessary biopsy. A difference in sNB of 0 indicates that adding a protein biomarker to CA19-9 in a prediction model has no added clinical value over using CA19-9 alone. A difference in sNB of lower than 0 (grey shaded region in the plots) indicates that adding a protein biomarker to CA19-9 would result in clinical harm compared with using CA19-9 only in the management of suspected PDAC.