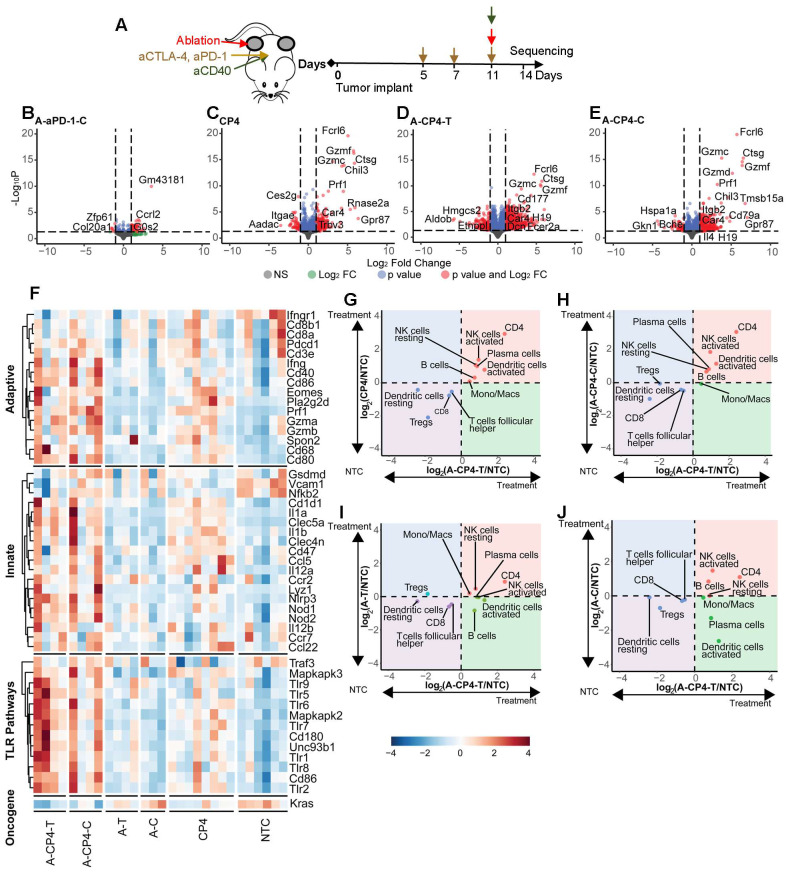
Figure 6.
Digital cytometry analysis in the MT4 model demonstrates the enhanced immune activation resulting from a four-component treatment combining ablation with CP4 (aCD40 + aPD-1 + aCTLA-4). A) Treatment protocol. Mice were treated with two doses of checkpoint inhibition priming prior to an application of checkpoint inhibitors with aCD40 and ablation each added in a subset of mice (n=4 each group) and compared to no treatment control (NTC) mice (n=4). Bulk RNA sequencing was performed 72 hrs after ablation. B-E) Volcano plots showing gene expression response to treatment combinations. B) Ablation + aPD-1 in the distant tumor (A-aPD-1-C) altered expression of 50 genes. C) CP4 altered expression of 285 genes. D-E) Ablation + CP4 resulted in D) 1379 differentially expressed genes in the treated (A-CP4-T) tumor and E) 475 differentially expressed genes in the distant (A-CP4-C) tumor. F) Ablation + CP4 upregulated genes in key immune pathways such as the adaptive immune (GO:0002819), innate immune (GO:0045088) and toll-like receptor (TLR) (GO:0002224) pathways and downregulated the Kras cancer gene in both the treated and contralateral tumors to a greater degree than systemic CP4 treatment alone. G-J) Digital cytometry was applied to bulk RNA sequencing data. Fold change from the NTC is plotted between ablation + CP4 in the ablated tumor (A-CP4-T) versus G) CP4, H) ablation + CP4 in the distant tumor (A-CP4-C), I) ablation-only in the treated tumor (A-T), and J) ablation-only in the distant tumor (A-C). Ablation + CP4 stimulated immune cell changes in both the treated and distant tumor sites, increasing CD4+ T cells and dendritic cell and NK-cell activation.