Table 2.
Toolpath parameters.
| Printing Parameter | Depiction | Description | Impact on dimensional accuracy identified in analysed studies from an increase (↑ top row) or decrease (↓ bottom row) in printing parameter value. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nozzle gap height (NGH) | 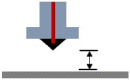 |
Also known as layer thickness, the measured displacement from the tip of the extruder nozzle to each successive layer of deposited material. NGH can also influence the defects listed: Circularity, Cylindricity, Porosity, and Surface Roughness. | ↑ | [10, 22, 25, 32, 33, 37, 46, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76] |
| ↓ | [12, 26, 27, 31, 34, 35, 36, 44, 45, 53, 54, 62, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112] | |||
| Filament volumetric velocity (FVV) | 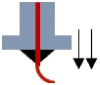 |
Also known as feed rate, the volume of material extruded through the nozzle per unit distance travelled. FVV can also influence the defects listed: Geometrical accuracy, Porosity, and Surface Roughness. | ↑ | [38, 67, 71, 100, 105, 113, 114], |
| ↓ | [73, 84, 103, 115] | |||
| Print head velocity (PHV) |  |
Also known as print speed, the velocity the extruder head traversers across the build envelope during deposition and non deposition. PHV can also influence the defects listed: Circularity, Geometrical accuracy, Surface Roughness, Shrinking, and Warping. | ↑ | [25, 31, 37, 53, 54, 61, 65, 72, 73, 88, 99, 100, 109, 114, 116, 117] |
| ↓ | [32, 34, 36, 68, 71, 76, 92, 106, 108, 112, 118] | |||
| Air Gap (AG) | 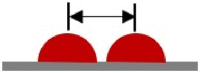 |
The measured lateral distance between the centre points of deposited adjacent filament strands. AG can also influence the defects listed: Geometrical accuracy, Porosity, and Surface Roughness. | ↑ | [12, 21, 22, 44, 86, 110, 119, 56] |
| ↓ | [22, 45, 46, 120] | |||
| Raster angle (RA) |  |
The angle between deposited adjacent strands with respect to the X axis. RA can also influence the defects listed: Geometrical accuracy and Surface Roughness. | ↑ | [21, 44, 60, 88, 119, 120, 121], |
| ↓ | [12, 22, 45, 46, 56, 66, 70, 78, 104, 110] | |||
| Road width (RW) | 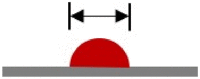 |
Also known as raster width, the width of a deposited stand, which is a function of the extruder nozzle diameter and toolpath parameters. RW can also influence the defects listed: Geometrical accuracy and Surface Roughness. | ↑ | [12, 22, 45, 53, 60, 61, 66, 83, 120, 120, 121] |
| ↓ | [21, 25, 27, 36, 44, 46, 56, 63, 64, 110, 119, 122] | |||
| Contour width (CW) | 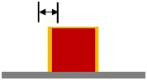 |
Also known as perimeters and number of shells, the thickness of the outer wall of a printed part. CW can also influence the defects listed: Geometrical accuracy and Surface Roughness. | ↑ | [10, 21, 28, 39, 46, 85, 121, 123] |
| ↓ | [10, 36, 38, 44, 65, 77, 87] | |||
| Contour print head velocity (CPHV) | 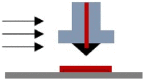 |
Similar to print head velocity, this sets the velocity of the extruder head whilst depositing the contours of the part. CPHV can also influence the defects listed: Geometrical accuracy, Surface Roughness, and Warping. | ↑ | [105] |
| ↓ | [67, 113] | |||
| Infill print head velocity (IPHV) | 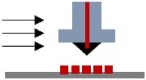 |
Similar to contour and print head velocity, this sets the velocity of the extruder head whilst depositing the infill layers of the part. IPHV can also influence the defects listed: Geometrical accuracy and Porosity. | ↓ | [113, 124] |
