Table 4.
Design parameters.
| Printing Parameter | Depiction | Description | Impact on dimensional accuracy identified in analysed studies from an increase (↑ top row) or decrease (↓ bottom row) in printing parameter value. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Build orientation (BO) | 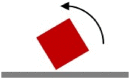 |
The chosen orientation of a part on the build platform prior to printing. This affects an array of factors such as build time, mechanical properties, and support structures. BO can also influence the defects listed: Anisotropy, Circularity, Geometrical accuracy, Porosity, Surface Roughness, and Warping. | ↑ | [10, 33, 46, 71, 79, 81, 100, 129, 130] |
| ↓ | [22, 32, 35, 44, 45, 60, 66, 69, 70, 72, 78, 85, 87, 96, 101, 110, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135] | |||
| Infill pattern (IP) | 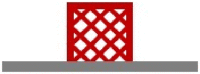 |
The internal architecture of the part, which affects mechanical properties, build time, printing cost, weight, and density. IP can also influence the defects listed: Geometrical accuracy and Surface roughness. | [33, 38, 39, 65, 77, 92, 95, 104, 122] | |
| Infill density (ID) | 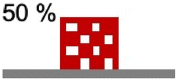 |
The volume of material printed inside the part, which also affects mechanical properties, build time, printing cost, and weight. ID can also influence the defects listed: Circularity, Geometrical accuracy, Porosity, and Surface Roughness. | ↑ | [28, 36, 37, 54, 62, 65, 68, 69, 88, 97, 104, 108, 118, 124, 134] |
| ↓ | [95, 96, 99, 109, 113, 128, 131, 133, 80, 93] | |||
| Build envelope position (BEP) | 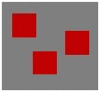 |
The location of the part on the build envelope. | [33, 107, 136] | |
