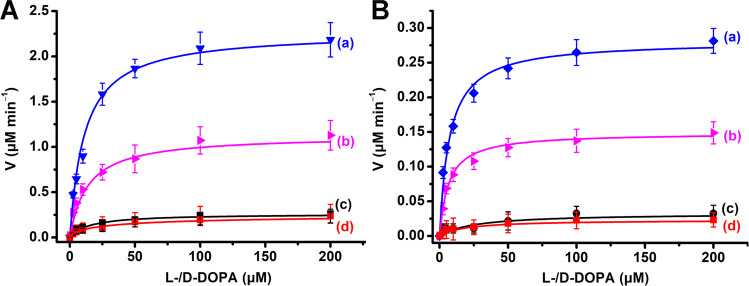
Figure 4.
(A) Rates corresponding to the (4)-pA-AuNPs (aptananozyme IV)-catalyzed oxidation of l-DOPA (a) and d-DOPA (b) by H2O2, 10 mM, to yield l-dopachrome and d-dopachrome in the presence of variable concentrations of l-DOPA and d-DOPA, respectively. (c, d) Rates corresponding to the oxidation of l-DOPA and d-DOPA in the presence of variable concentrations of l-/d-DOPA by H2O2, using the separated pA-AuNPs and DBA, respectively. (B) Rates corresponding to the aptananozyme IV-catalyzed oxidation of l-DOPA (a) and d-DOPA (b) by H2O2 generated by the aerobic oxidation of glucose, 50 mM, to yield l-dopachrome and d-dopachrome in the presence of variable concentrations of l-DOPA and d-DOPA, respectively. (c, d) Rates corresponding to the oxidation of l-DOPA and d-DOPA in the presence of variable concentrations of l-/d-DOPA by H2O2 generated by the aerobic oxidation of glucose, 50 mM, using the separated pA-AuNPs and DBA, respectively. In all experiments, the concentration of the aptananozyme IV corresponds to 5 nM. Error bars are derived from N = 3 experiments.