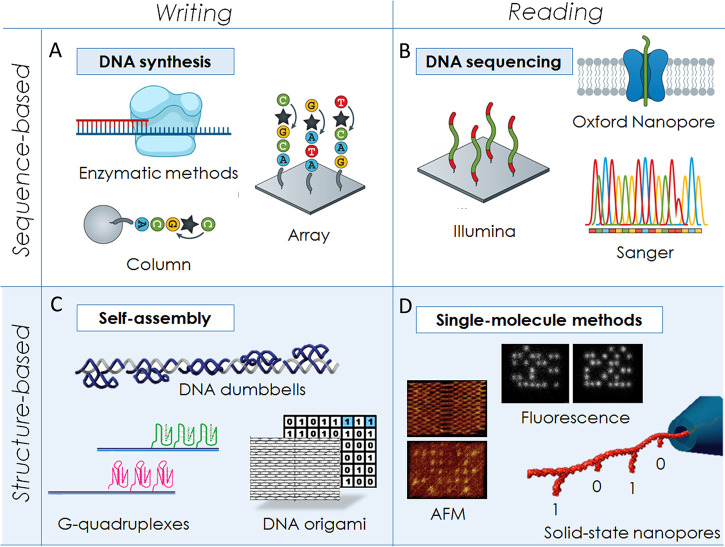
Figure 2.
Comparison of the main differences between sequence-based (A,B) and structure-based DNA data storage (C,D), as has been presented in the literature to date. (A,B) Sequence-based storage relies on the de novo synthesis of DNA strands and the subsequent sequencing of these entities is performed using next-generation methods. Image adapted with permission from ref (12). Copyright 2019 Springer Nature. (C) By contrast, structure-based methods utilize self-assembly, which means that the information is encoded into their three-dimensional shape. Images adapted with permission: ref (21), copyright 2016 Springer Nature; ref (22), under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License (CC BY), copyright 2021 Springer Nature. (D) These shapes can then be read off using single-molecule methods, including fluorescence, atomic force microscopy, and nanopore techniques. Image adapted from ref (23). Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society.