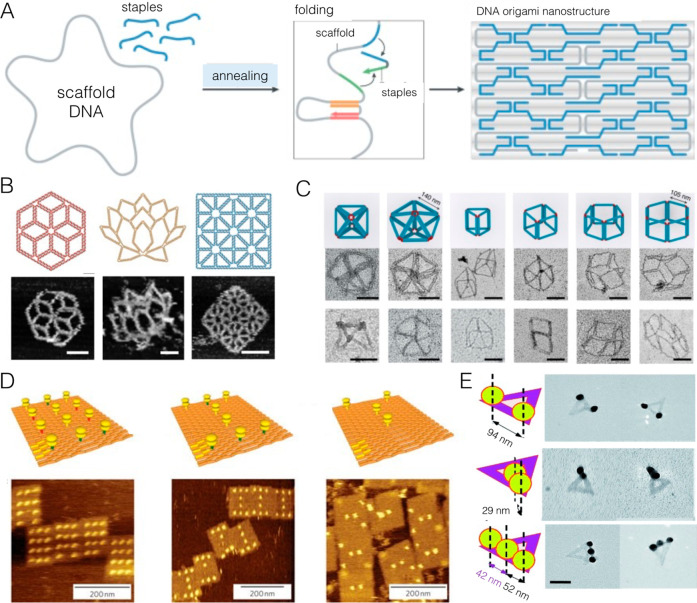
Figure 8.
DNA nanostructures are data storage architectures. (A) DNA origami leverages the specific base-pairing motifs of DNA to create arbitrary structures. When a long scaffold strand (several thousand nucleotides in length) is combined with hundreds of short “staple” strands, complementary regions on the different strands will hybridize, thereby folding the scaffold into a desired conformation. These structures can then be examined using (B) atomic force microscopy or (C) electron microscopy, for example. (D) Data can be written onto DNA origami sheets through the site-specific addition of proteins; the data may be read using AFM. (E) Nanoparticles can also be controllably positioned on DNA origami with nanometer-scale resolution, which enables data writing with cryo-EM readout. (A) Image reproduced with permission from ref (108). Copyright Springer Nature 2021. (B) Image reproduced with permission under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License (CC BY) from ref (109). Copyright 2019 AAAS. (C) Image reproduced with permission from ref (110). Copyright 2020 Springer Nature. (D) Image reproduced with permission from ref (111). Copyright 2010 Springer Nature. (E) Image reproduced with permission from ref (112). Copyright 2010 Wiley-VCH.