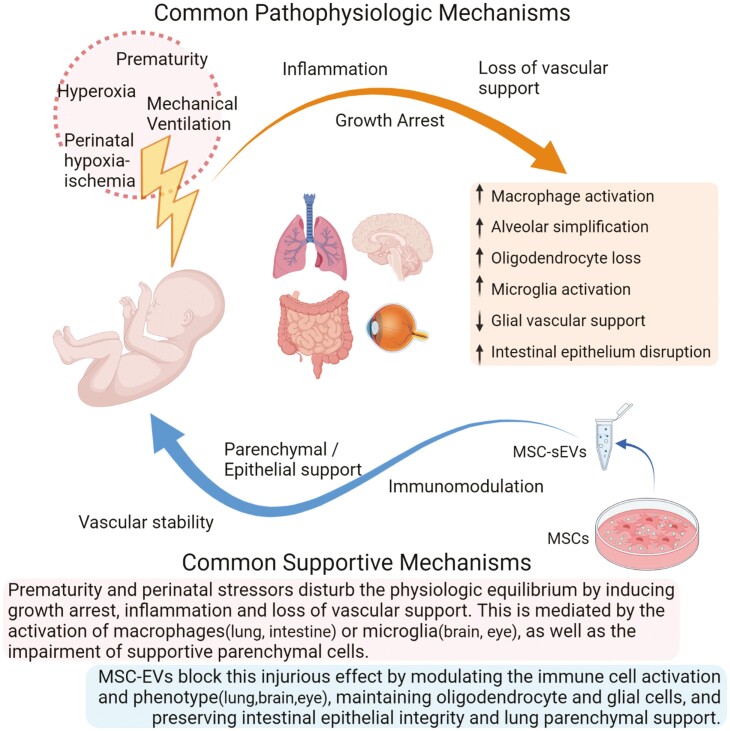
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the common pathophysiologic mechanisms shared by neonatal diseases, as well as the common supportive effects of MSC-EV treatment. Prematurity and perinatal stressors disturb the physiologic equilibrium by inducing growth arrest, inflammation and loss of vascular support. This is mediated by the activation of macrophages (lung, intestine) or microglia (bran, eye), as well as the impairment of supportive parenchymal cells. MSC-EVs block this injurious effect by modulating the immune cell activation and phenotype (lung, brain, and eye), maintaining oligodendrocyte and glial cells, and preserving intestinal epithelial integrity and lung parenchymal support.