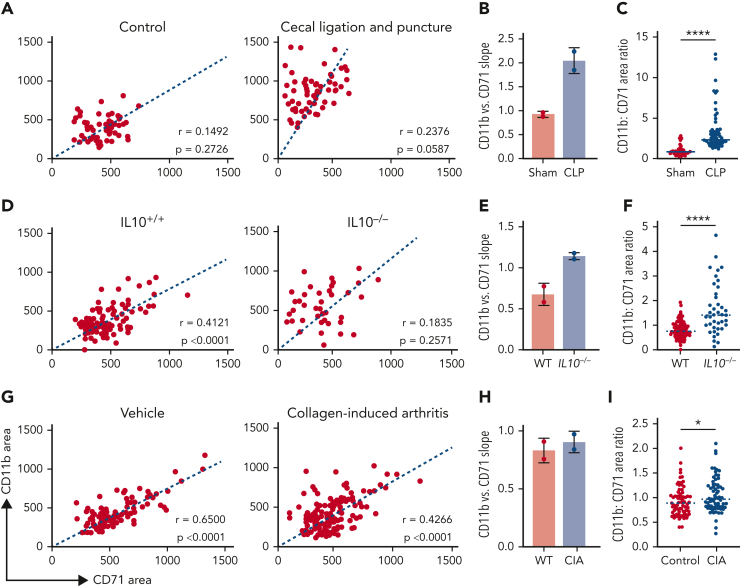
Figure 5.
The balance between CD71+ erythroblasts and CD11b+ granulocytes in the EBIs is altered in AoI. EBI analysis was performed for 3 different models of AoI. Representative plots of CD11b+ area vs CD71+ area for each of the 3 models of AoI and corresponding controls are shown in order of decreasing acuity and consequently decreasing CD11b vs CD71 slope. Each point represents an EBI observed by IFC; all EBIs observed in one biological replicate are shown. Spearman correlation coefficient r values along with corresponding P values for correlation are shown on the graphs. (A) Cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) model resembles sepsis and shows the most dramatic increase in CD11b+ vs CD71+ slope. (B) Quantification of the slope of CD11b+ vs CD71+ area in control and CLP (n = 2, mean ± SD is shown in the bar graphs). (C) Ratio of CD11b+:CD71+ within each EBI (median shown in graph; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001 by Mann-Whitney test). (D) IL10−/− mice, when they develop inflammatory bowel disease, show a moderate increase in CD11b vs CD71 slope. (E) Quantification of the slope of CD11b vs CD71 area in control and IL10−/− (n = 2; mean ± SD is shown in the bar graphs). (F) Ratio of CD11b+:CD71+ within each EBI (median shown in graph; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001 by Mann-Whitney test). (G) Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) models show mild inflammation relative to the CLP and IL10−/− with colitis models associated with a mild increase in CD11b+ vs CD71+ slope. (H) Quantification of the slope of CD11b vs CD71 area in control and CIA (n = 2, mean ± SD is shown in the bar graphs). (I) Ratio of CD11b+:CD71+ within each EBI (median shown in graph, ∗P < .05 by Mann-Whitney test). No statistical test was performed for the comparison of slopes in B, E, and H, in which 2 samples for each experimental and each control mouse model of AoI were analyzed.