Extended Data Fig. 4. LSD1-BAF interaction in endocrine sensitive and resistant cells.
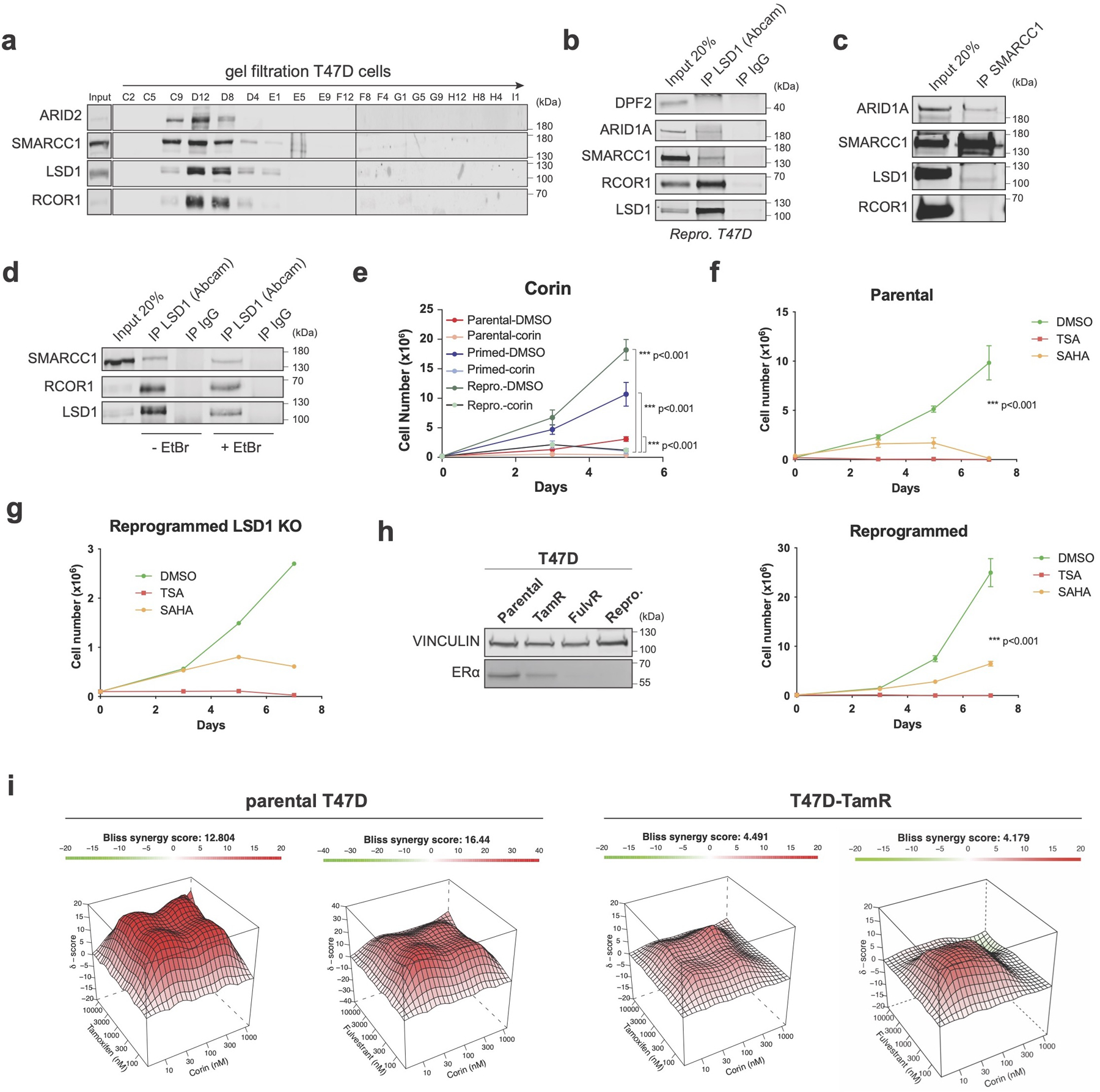
a, Superose 6 gel filtration in parental cells showing co-elution of LSD1, RCOR1, and members of the SWI/SNF complex (SMARCC1 and ARID2). b, LSD1 IP with SWI/SNF subunits in reprogrammed T47D. Note that the DPF2-LSD1 interaction was also not detected by LC-MS/MS (Fig. 2e). c, SMARCC1 IP with LSD1 in reprogrammed T47D. d, The LSD1-SMARCC1 interaction is DNA-independent. EtBr, ethidium bromide1. e-f, Proliferation of T47D treated with 1µM corin for 5 days (e), and TSA or SAHA for 7 days (f), n = 3 biological independent replicates. Data are presented as mean values + SEM, p-value < 0.001 (two-way ANOVA). g, Proliferation of WT and LSD1 KO reprogrammed T47D treated with TSA or SAHA for 7 days, n = 2 independent experiments. h, ERα WB in parental and endocrine resistant T47D lines with VINCULIN as a loading control. i, Synergy maps of parental and TamR T47D treated with tamoxifen and corin, or fulvestrant and corin. The 3D synergy matrix was generated with SynergyFinder 2.0, n = 3 biological independent replicates. Uncropped images are available as source data.
