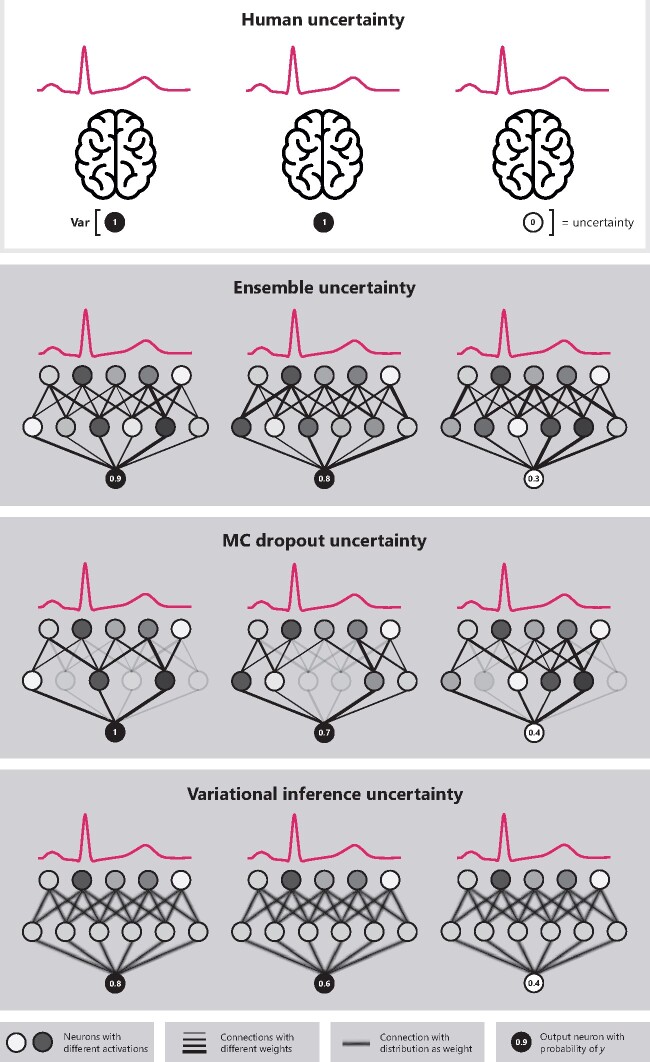
Figure 1.
Overview of the uncertainty estimation concept and the epistemic uncertainty estimation methods. All methods work similarly to human uncertainty (in the top box, illustrated as several brains), where there are multiple reviewers interpreting the same electrocardiogram. The uncertainty is then calculated as the variance over these different predictions for the same electrocardiogram. With deep neural networks multiple predictions can be achieved using ensembles (i.e. training the same network multiple times), MC dropout (i.e. removing some nodes randomly during prediction), or variational inference (i.e. sampling from the same network with distributions as weights multiple times).