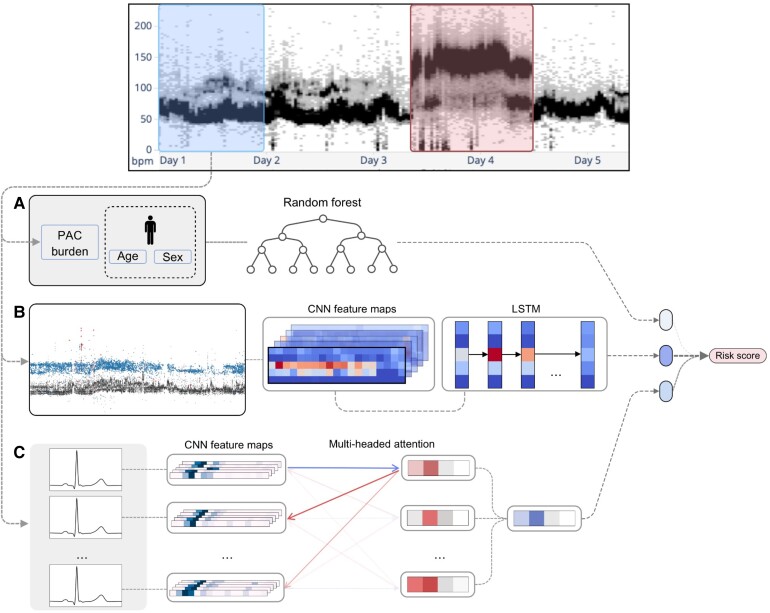
Figure 2.
Model’s diagram. The first 24 h from a Holter are used to derive inputs for the different models while the following 14 days are used to assign a label. (A) Patient age, sex, and 24 h pre-mature atrial contraction burden are passed into a random forest classifier to predict an age, sex, and pre-mature atrial contraction score. (B) A convolutional neural network is used to extract feature maps from a heart rate plot, which are passed into a long short-term memory layer as temporal features to predict a heart rate-deep neural network score. (C) The Holter is split into sequences of 80 consecutive beats which are individually passed into a convolutional neural network for feature extraction. Then an attention layer identifies relationships between beats within a sequence to predict a score; the average prediction of all sequences is used as the Beat-deep neural network score. The prediction scores from each model are then passed into a logistic regression classifier to generate a final risk score.