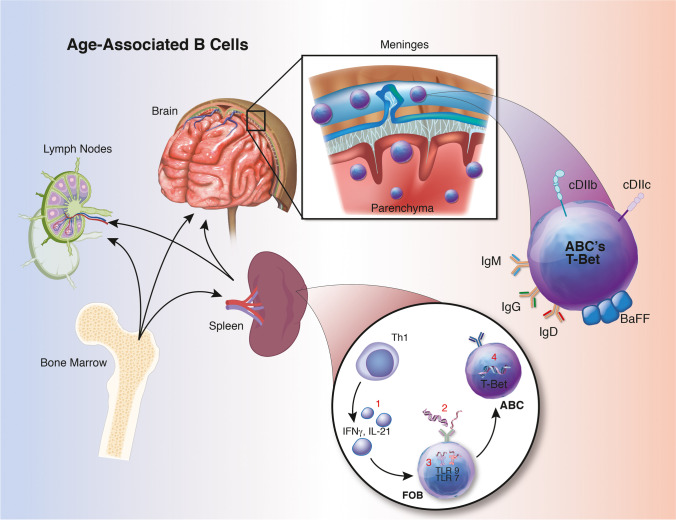
Fig. 2.
Overview of age-associated B cells (ABCs), including a schematic of development within the spleen: (1) follicular B cells (FOB; also include MZ populations) receive signals from Th1-type cytokines or other nearby interactions, and (2) uptake either endogenous double-stranded (DS)DNA or RNA-associated antigen. (3) These antigens activate toll-like receptor (TLR) 9 and TLR7 and following several divisions and expression of T-bet become an ABC. ABCs can be found in several lymphoid organs, the meninges, and brain parenchyma