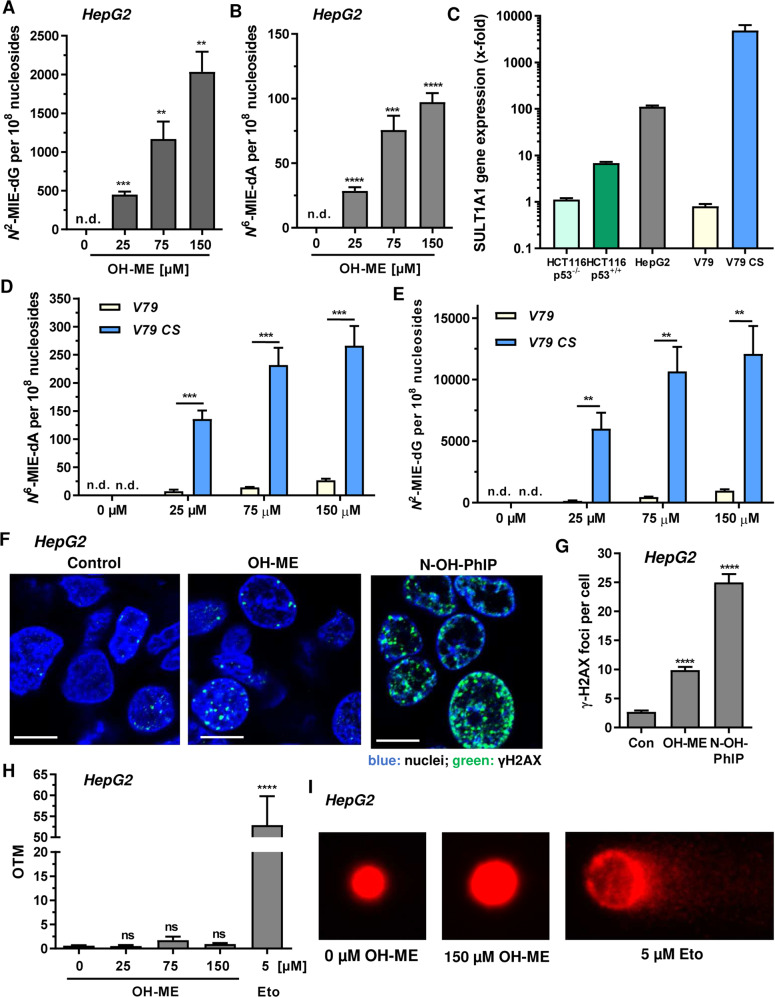
Fig. 1. Impact of SULT1A1 on DNA damage induction by 1′-OH-methyleugenol in human liver cells and hamster fibroblasts.
A, B Formation of N2-MIE-dG and N6-MIE-dA adducts in human HepG2 cells. Cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of OH-ME as indicated for 24 h. Isolated genomic DNA was digested to nucleosides and adduct levels were determined by UPLC-mass spectrometry using stable isotope dilution analysis (n = 4). C SULT1A1 level in HepG2 cells and further cell lines used in this study. Gene expression was assessed by qPCR (n = 3). D, E Formation of N2-MIE-dG and N6-MIE-dA adducts in parental V79 cells and V79 cells proficient for human CYP1A2 and SULT1A (V79 CS). Cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of OH-ME as indicated for 24 h. Isolated genomic DNA was digested to nucleosides and adduct levels were measured by UPLC-mass spectrometry using stable isotope dilution analysis (n = 4). F Formation of the DNA damage marker γH2AX in HepG2 cells 24 h upon treatment with 150 µM OH-ME. DMSO was used as solvent control, while 50 µM N-OH-PhIP was included as positive control. Representative confocal microscopy images are shown (scale bar: 10 µm). G The number of γH2AX foci per nucleus were determined by ImageJ software (n = 3, 50–100 cells per experiment). H Analysis of DNA strand break induction by OH-ME. HepG2 cells challenged with increasing concentrations of OH-ME for 24 h were subjected to the alkaline Comet assay. Etoposide was included as positive control. OTM: olive tail moment (n = 3). I Representative images obtained by the Comet assay. Data in A–H are given as mean + SEM. Not significant, p > 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. n.d. indicates not detected.