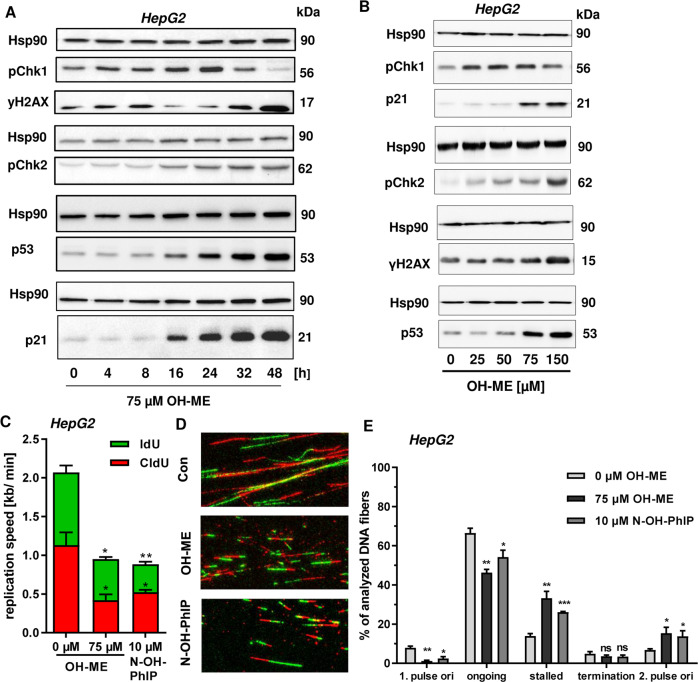
Fig. 2. Activation of the DNA damage response by ME-derived DNA adducts and replication stress in human liver cells.
A Time-dependent DNA damage response in HepG2 human liver cells. Cells were exposed to 75 µM OH-ME and incubated for up to 48 h. Samples were collected as indicated and subject to western blot analysis of pCHK1, γH2AX, pCHK2, p53, and p21. Hsp90 was detected as loading control. A representative blot is shown. B Concentration-dependent DNA damage response in HepG2 cells triggered by OH-ME. Cells were challenged with up to 150 µM OH-ME for 24 h. Subsequently, cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blot detection as described in (B). A representative western blot is shown. C Impact of OH-ME on replication speed. HepG2 cells were treated for 24 h and replication speed was determined by DNA fiber assay using confocal microscopy. D Representative DNA fiber tracks of HepG2 cells exposed to OH-ME or N-OH-PhIP. E Distribution of replication structures assessed by the DNA fiber assay in HepG2 cells exposed to OH-ME or N-OH-PhIP for 24 h. Data in C and E are given as mean + SEM (n = 3). Not significant, p > 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001.